The rapid proliferation of Non-Human Identities (NHIs) accross decentralized secrets ecosystems exposes organizations to significant operational inefficiencies and critical security vulnerabilities.
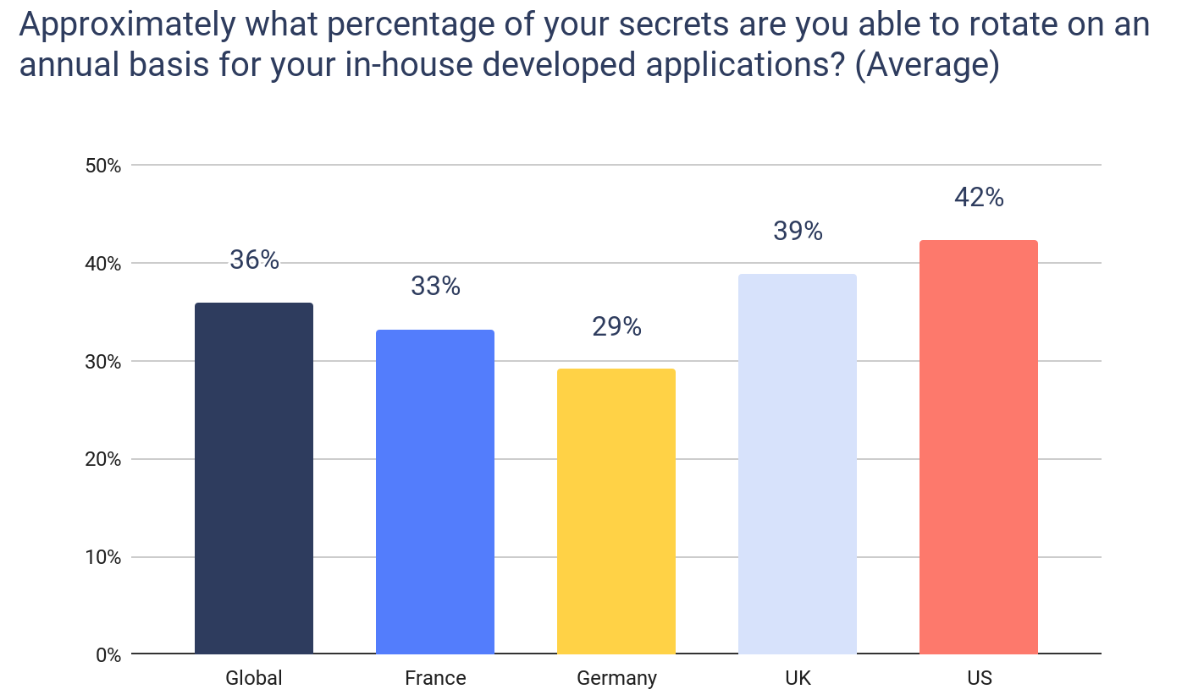
Vaults are essential for securing Non-Human Identities by centralizing secrets storage (API keys, tokens, and certificates), enforcing access controls, and automating secrets rotation to reduce exposure risks and ensure compliance. Yet, as Voice of Practitioners (VoP) respondents reported, many organizations face vault sprawl, using an average of six different secret management instances across teams. This fragmentation creates silos, complicates management, and undermines consistent security practices.
GitGuardian's NHI solutions directly address these challenges. We empower organizations to secure their NHIs effectively with real-time visibility into secrets usage, centralized policy enforcement and proactive risk detection.
GitGuardian is thrilled to announce a key enabler of this strategy: the integration with major secrets managers HashiCorp Vault, CyberArk Conjur, AWS Secrets Manager, Google Cloud Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, Akeyless Vaultless Secrets Management, and Delinea Secrets Server.
These integrations give organizations comprehensive insights into their secrets across distributed infrastructures, enabling them to prioritize and remediate incidents more effectively—ultimately strengthening their NHI security across the most complex environments.
The Role and Limitations of Vaults in Securing NHIs
Vaults as the Backbone of Secrets Management
Unlike human identities, which are tied to specific departments, NHIs can be created by anyone in the organization, often without following company-defined policies. This lack of visibility often stems from a mix of inadequate training and the perception that security measures hinder productivity.
Consequently, organizations lack a consolidated source of truth for NHIs and their tied secrets. Vaults partially address this gap by centralizing the storage of secrets, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access, and facilitating efficient rotation. This trend is evident across industries— 77% of the VoP respondents declared their organization is either investing in or planning to invest in secrets management solutions by 2025.
Limited Vault Adoption and Challenges
In highly distributed environments with sprawling NHIs, vaults provide the foundational infrastructure needed to manage secrets securely and maintain operational efficiency. However, they only solve some of the challenges around secrets security. Most vaults lack visibility into:
- Where each secret is used, and what is the tied identity
- The permissions each secret grants across systems.
- Secrets stored outside the vault, such as those hardcoded in applications or mistakenly pushed to public repositories.
Additionally, their adoption is hindered by:
- Complex Tooling: Vaults often require extensive configuration, deterring teams from full adoption.
- Lack of Operational Support: Unclear onboarding processes and policies lead to inconsistent usage.
- Developer Perception: Vaults are sometimes seen as barriers to productivity, pushing teams to insecure workarounds like hardcoding secrets in code.
This challenge is compounded by the fact that organizations rely on multiple vault solutions—legacy systems, third-party vaults, and modern cloud-native vaults—that are rarely managed by a single team.
As a result, secrets remain scattered across environments, increasing the risk of exposure and leaving critical systems vulnerable to breaches.
When Vaults Fall Short
"Today, it's hard to perform an end-to-end mapping for a single secret. It would take me at least 2-3 full-day of investigation."
an AppSec Engineer at a prominent hedge fund
Even when organizations adopt vaults, common pitfalls limit their effectiveness :
- Duplicated secrets: Multiple instances of the same secret can appear in different vaults, complicating secret rotation.
- Inconsistent Secrets Rotation: While one team may rotate secrets regularly, another team using a different vault might not. This can slow incident response when immediate rotation is needed to contain an active threat.
- Poor Visibility: Without centralized oversight, tracking which secrets are active, stale, or overprivileged becomes a major obstacle, increasing misuse risks.
- Limited Auditing and Monitoring: Logs often go unaudited due to the absence of automated tools or the overwhelming volume of log data, resulting in missed anomalies and vulnerabilities.
These challenges demonstrate that vaults alone are insufficient to secure NHIs comprehensively. To overcome these limitations, organizations need tools that extend vault functionalities.
Secrets Management Best Practices for Enterprise Implementation
Implementing effective secrets management requires adherence to fundamental security principles that extend beyond basic vault deployment. According to OWASP guidelines, organizations must prioritize high availability to ensure secrets management systems can service traffic reliably during critical incidents. When applications depend on database credentials and API keys, poor performance can degrade availability or increase startup times significantly.
Access control represents another cornerstone of secure implementation. The principle of least privilege must be rigorously applied, ensuring engineers cannot access all secrets within the management system. Fine-granular access controls on each object and component prevent unnecessary exposure while maintaining operational efficiency. Organizations should also implement centralized standardization across teams—even when using multiple secret management solutions. This approach ensures maintainability during incidents while providing clear documentation about secret purposes and locations.
Effective secrets management also demands robust auditing capabilities to track secret access patterns, rotation schedules, and usage across distributed environments. These practices form the foundation for preventing credential leaks and maintaining organizational security posture.
Common Secrets Management Anti-Patterns and Mitigation Strategies
Despite widespread vault adoption, organizations frequently encounter dangerous anti-patterns that undermine their secrets security posture. Hardcoded credentials remain pervasive across DevOps environments, with secrets embedded directly in source code, configuration files, and automation scripts. These practices create significant backdoors that attackers can exploit through simple scanning tools and dictionary attacks.
Secret sprawl represents another critical challenge, where identical credentials appear across multiple systems without centralized tracking. This fragmentation complicates rotation procedures and incident response, as security teams struggle to identify all instances of compromised secrets. Organizations often discover that services share the same secrets, making it nearly impossible to determine the source of a breach.
Manual rotation processes introduce human error and inconsistent security hygiene. Without automated lifecycle management, secrets frequently remain active beyond their intended lifespan, creating unnecessary exposure windows. Additionally, siloed management approaches across different platforms prevent holistic oversight, leaving security gaps that attackers can exploit.
Mitigation requires implementing automated discovery tools to identify embedded credentials, establishing centralized rotation schedules, and enforcing consistent policies across all platforms and teams.
Enhancing Your Secrets Management Strategy with GitGuardian's Multi-Vault Integrations
Centralized Secrets Management Across Vaults
Managing secrets in today's fragmented environments often requires organizations to use multiple secrets management platforms. GitGuardian integrates with the industry's leading vault solutions to provide centralized visibility and seamless management:
- HashiCorp Vault: Renowned for its scalability and flexibility, HashiCorp Vault is a top choice for enterprises and cloud-native environments.
- CyberArk Conjur: A cornerstone in securing DevOps pipelines, CyberArk Conjur automates secrets management for high-security environments.
- AWS Secrets Manager: Designed for native integration with AWS services, AWS Secrets Manager allows secure storage and lifecycle management of secrets within cloud ecosystems.
- Google Cloud Secrets Manager: Optimized for GCP environments, this platform simplifies secrets management for cloud-native workloads.
- Azure Key Vault: A pivotal tool for securing secrets in Microsoft Azure environments, Azure Key Vault also supports encryption keys and certificates for enhanced security.
- Delinea Secret Server: A robust secrets manager designed for enterprises, supporting extended Priviledged Access Management (PAM).
- Akeyless Vaultless Secrets Management: A solution that eliminates the need for a traditional vault by using distributed cryptography to manage and secure secrets.
Capabilities of GitGuardian's Multi-Vault Integration
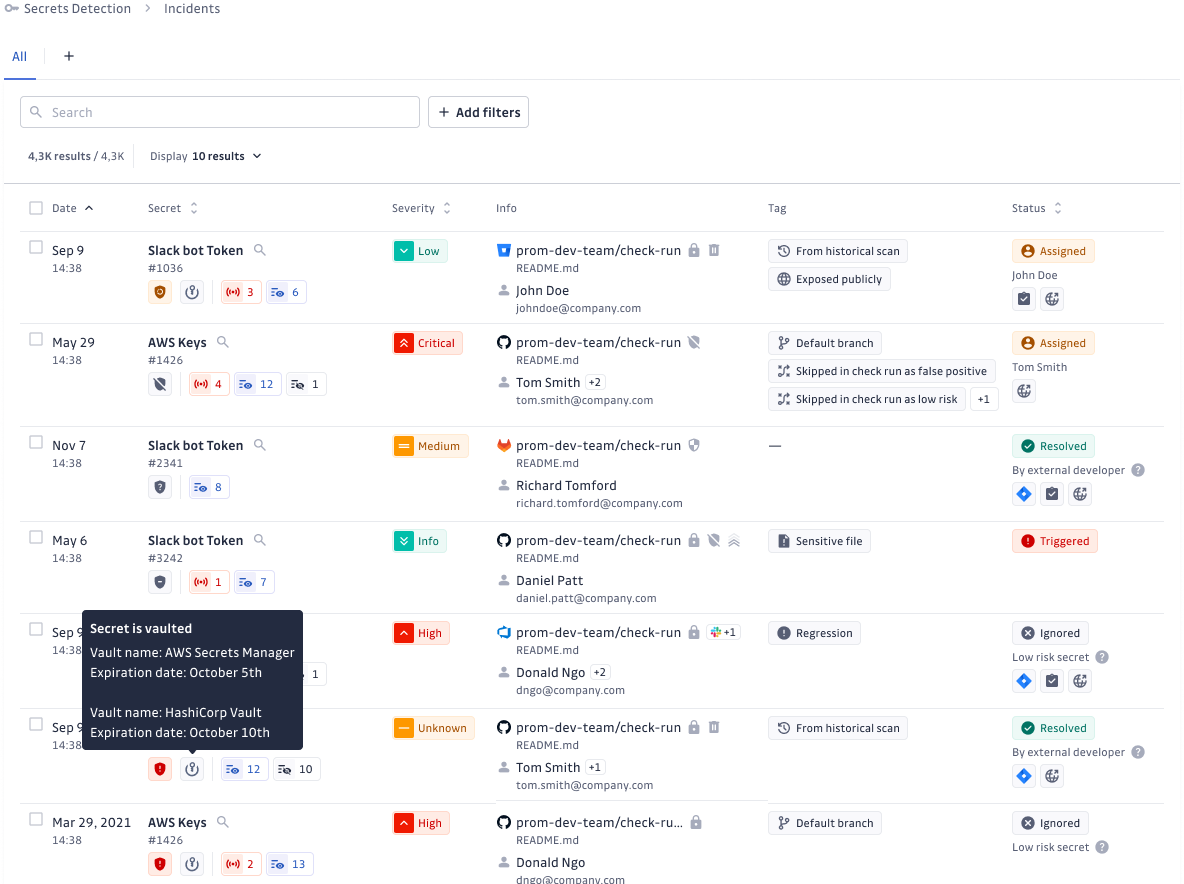
GitGuardian vault integrations extend their capabilities with robust solutions for several key use cases:
- Enumerating Vaulted Secrets: GitGuardian provides a comprehensive, centralized view of secrets across all integrated vaults. Teams can better track and manage their secrets inventory, ensuring no secrets are left unmonitored.
- Detecting and Vaulting Exposed Secrets: GitGuardian scans internal perimeters, such as codebases, CI/CD pipelines, and productivity tools, to identify exposed secrets. Upon detection, GitGuardian alerts security teams, allowing them to trigger the vaulting of exposed secrets, and initiate rotation workflows to mitigate risks.
- Detecting Public Leaks: Since 2017, GitGuardian has monitored GitHub, the world's largest developer platform, and uncovered tens of millions of publicly exposed secrets. Teams can periodically check their vaulted secrets against GitGuardian's proprietary database of public leaks, ensuring that compromised secrets are identified and rotated promptly.
- Identifying Security Risks: Stale, over-privileged, or unused secrets are flagged to help teams prioritize their remediation efforts. This proactive approach ensures that high-risk secrets are addressed before they can be exploited.
- Incident Prioritization: When secret incidents occur, GitGuardian associates them with affected vault entries, enabling security teams to assess the scope of exposure quickly. More context accelerates incident resolution and minimizes potential damage.
- Practical Remediation Guidance: GitGuardian provides actionable steps to enforce vault usage, rotate, and manage vaulted secrets. These recommendations streamline remediation workflows and reduce the efforts required to address security incidents.
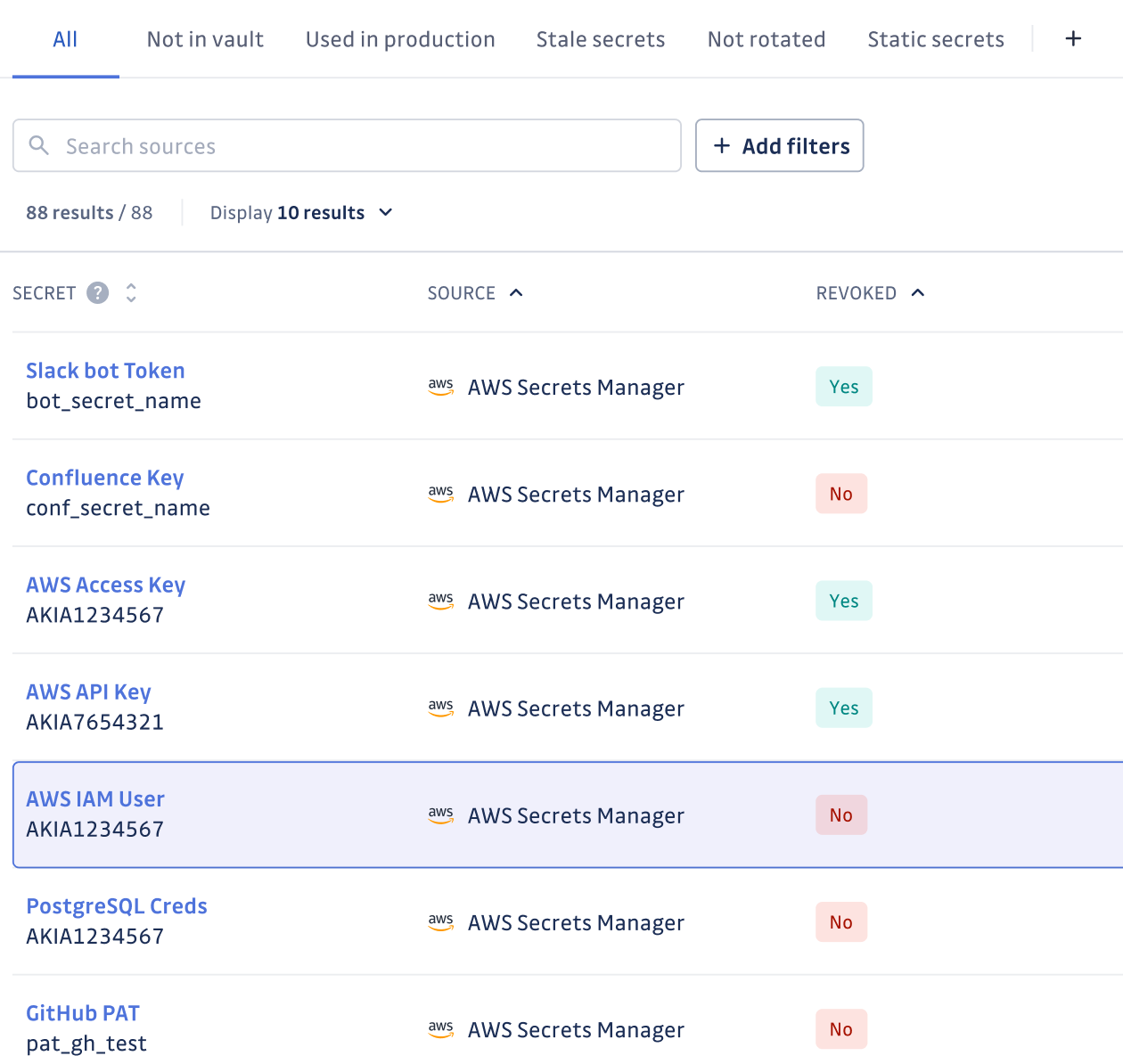
Secrets Management Architecture for Multi-Cloud Environments
Modern enterprises operating across multiple cloud providers face unique architectural challenges in implementing comprehensive secrets management. Google Cloud Secret Manager, AWS Secrets Manager, and Azure Key Vault each offer native capabilities, but organizations require unified governance strategies to prevent fragmentation and ensure consistent security policies.
Effective multi-cloud architecture demands establishing a primary secrets management layer that can federate with cloud-native solutions while maintaining centralized oversight. This approach enables teams to leverage cloud provider optimizations while ensuring enterprise-wide visibility and control. Organizations must also address cross-cloud secret sharing scenarios where applications in one environment require credentials from another provider's ecosystem.
Network segmentation becomes critical in multi-cloud deployments, ensuring secrets transit occurs over encrypted channels with appropriate access controls. Implementation should include automated synchronization mechanisms that maintain secret consistency across environments while respecting each cloud provider's security boundaries.
The architecture must also accommodate disaster recovery scenarios where primary secrets management systems become unavailable. This requires implementing redundant systems and clear failover procedures that maintain security standards during crisis situations while enabling rapid service restoration.
Accommodating the Complexity of Large Organizations
"While vaults play a key role in secrets management, they aren't sufficient to address the full spectrum of secrets security challenges. Our integrations take those platforms to the next level, ensuring enterprises can centralize their secrets management, reduce risks, and save on operational costs."
Eric Fourrier, CEO of GitGuardian
In large, distributed organizations, effectively managing secrets is no longer just about securing them—it's about enabling a unified governance for NHIs.
Onboarding and Vault Adoption
Challenges in onboarding teams to secrets management
Adopting vaults at scale is often hindered by lengthy and complicated setup processes. It discourages developers from integrating vaults into their workflows.
GitGuardian simplifies onboarding
By enforcing centralized security policies during onboarding, GitGuardian ensures compliance from day one. Platform engineers can identify teams and environments with inconsistent practices, and promote uniform standards across the organization.
Impact
Through simplified onboarding, GitGuardian minimizes risks caused by disparate practices and ensures that every team seamlessly integrates secure workflows. This approach lays the foundation for unified secrets governance from the outset.
"We have approximately 3,000 to 4,000 secrets in our vaults, but this is merely a drop in the ocean. I would expect at least 100 times more."
Head of DevOps at a leading automotive parts manufacturer.
Secrets Consolidation and Migration
The problem with vault sprawl
As organizations grow, they often deploy multiple vaults, resulting in redundant systems that increase costs and operational complexity, obscure secrets visibility, and make compliance more difficult.
GitGuardian simplifies vault architecture
GitGuardian enables organizations to consolidate secrets into fewer vaults with:
- Centralized oversight: Leverage a single-pane-of-glass to provide better oversight and ensure compliance.
- Secure migrations: Move secrets between vaults with minimal disruption, reducing downtime for critical systems.
- Cost reduction: Reduce operational expenses by identifying unused or redundant vaults to deactivate them.
- Visibility into secrets redundancies: Flag duplicate or outdated secrets to streamline consolidation efforts.
Impact
By consolidating secrets into fewer vaults, organizations achieve centralized governance, streamline team oversight, and significantly reduce operational expenses.
Streamlining Multi-Vault Operations for Complex Systems
The complexity in multi-vault environments
Managing secrets across multiple vaults poses significant challenges, such as monitoring access logs, assessing compliance with industry standards, or ensuring SLAs are met.
GitGuardian's role in simplifying operations
GitGuardian standardizes rotation schedules, access controls, and auditing practices across all integrated vaults. Organizations can:
- Implement cross-vault policies to enforce consistent security practices across distributed infrastructures.
- Track access patterns and rotation history to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Impact
GitGuardian's solutions reduce the manual burden on teams, enhance operational efficiency, and strengthen governance. This approach enables organizations to scale secrets management seamlessly while maintaining strong security standards
Securing your infrastructure with GitGuardian's secrets managers integrations
Managing secrets in complex environments is challenging, with vault sprawl, fragmented management, and inconsistent practices creating significant security risks. GitGuardian's multi-vault integration is a core component of its broader NHI Security strategy, designed to unify governance across platforms and environments. By streamlining operations and improving visibility, GitGuardian empowers organizations to achieve robust security and operational resilience.
Looking ahead, GitGuardian is committed to expanding its integration coverage and capabilities to tackle evolving challenges, including enhanced automation, advanced analytics, and faster incident response. These advancements will ensure organizations stay ahead in securing their NHIs.
Ready to take control of your secrets management? Contact our Customer Success team to experience the benefits of GitGuardian's multi-vault integration today and build a more secure, resilient infrastructure.
FAQ
How does GitGuardian's multi-vault integration address secrets sprawl in large organizations?
GitGuardian's multi-vault integration provides centralized visibility and management across multiple secrets management platforms. By consolidating secrets inventories, detecting redundancies, and standardizing policies, organizations can reduce operational complexity, minimize blind spots, and enforce consistent secrets management practices across distributed teams and environments.
What are the main limitations of relying solely on vaults for secrets management?
Vaults centralize secret storage but often lack visibility into secret usage, permissions, and secrets stored outside the vault. They may also suffer from inconsistent adoption, duplicated secrets, poor rotation practices, and limited auditing, leaving organizations exposed to operational inefficiencies and security risks.
How does GitGuardian help with secrets rotation and incident response?
GitGuardian enables organizations to detect exposed, stale, or over-privileged secrets and provides actionable remediation guidance, including automated rotation workflows. By associating incidents with specific vault entries and providing context, GitGuardian accelerates incident response and helps teams contain threats more effectively.
What best practices should enterprises follow for effective secrets management in multi-cloud environments?
Enterprises should implement a primary secrets management layer that federates with cloud-native solutions, enforce centralized access controls, and maintain robust auditing. Automated synchronization, encrypted secret transit, and disaster recovery planning are essential to ensure consistent security and high availability across multi-cloud architectures.
How does GitGuardian improve onboarding and adoption of secrets management solutions?
GitGuardian streamlines onboarding by enforcing centralized security policies and providing visibility into onboarding gaps. This ensures all teams integrate secure workflows from the outset, reducing inconsistent practices and laying the foundation for unified secrets governance across the organization.
What anti-patterns commonly undermine secrets management, and how can they be mitigated?
Common anti-patterns include hardcoded credentials, secret sprawl, manual rotation, and siloed management. Mitigation strategies involve automated discovery of embedded secrets, centralized rotation schedules, and enforcing consistent policies and auditing across all platforms to reduce risk and improve incident response.
How does GitGuardian support compliance and auditing requirements for secrets management?
GitGuardian provides comprehensive auditing capabilities, tracking secret access, rotation history, and usage across integrated vaults. This centralized oversight supports compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements, while automated monitoring reduces manual effort and ensures timely detection of anomalies.