Is agentic AI the productivity revolution we've been waiting for, or a security nightmare in the making? With AI agents now outnumbering humans and secrets proliferating across enterprise systems, the answer isn't simple. Read our insights from SecDays {France} 2025.
When industry leaders gathered at SecDays France to discuss agentic AI, the question wasn't whether this technology would transform business operations—it was whether organizations could harness its power without falling victim to an unprecedented security nightmare.
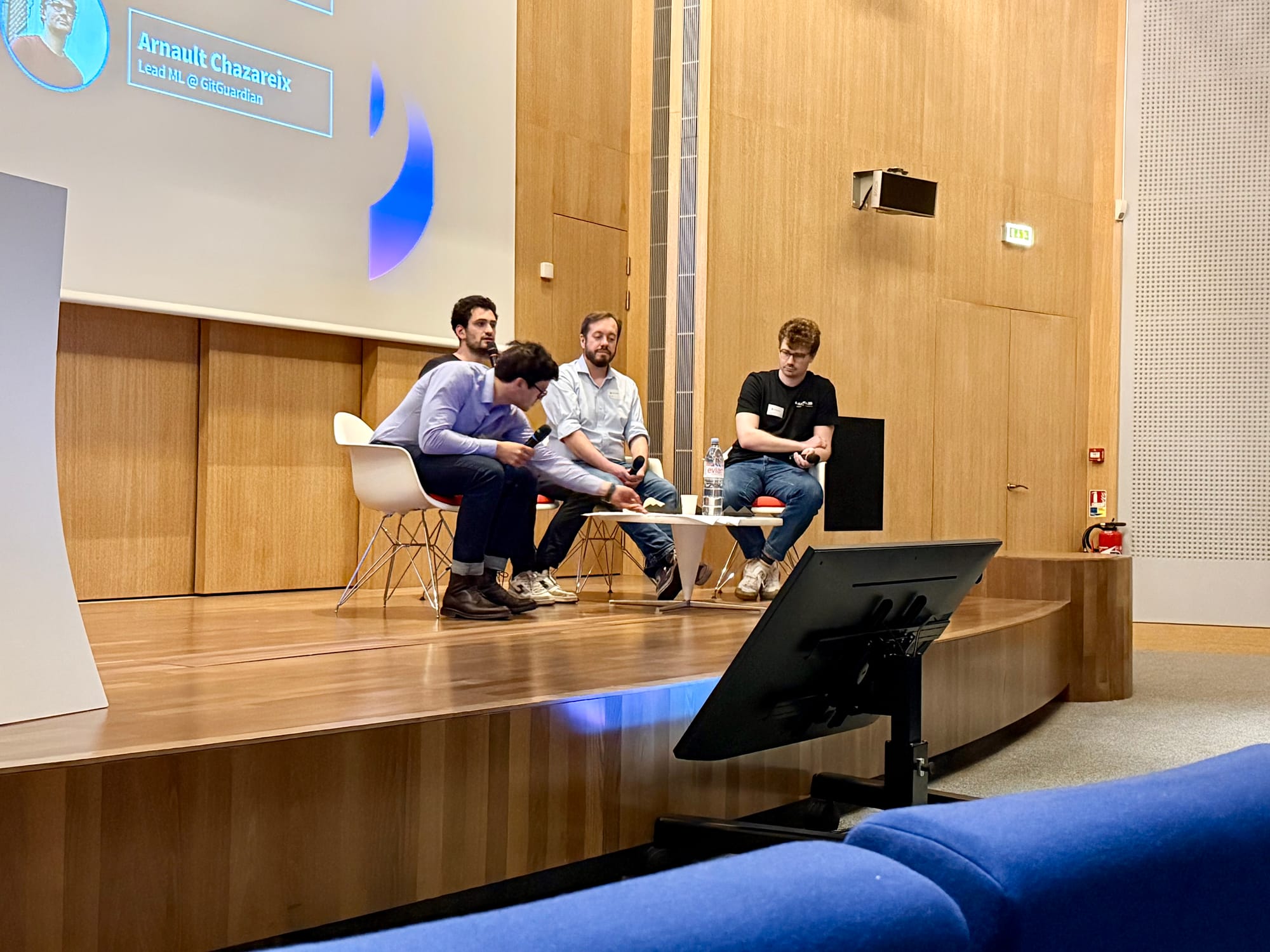
Eric Fourrier, Gilles Walbrou (DataDome), Noé Achache (Theodo) and Arnaud Chazareix from GitGuardian at the AgenticAI roundtable at SecDays France 2025

Beyond Workflows: Understanding the Agentic Revolution
Unlike the deterministic workflows that have dominated enterprise automation, agentic AI represents a paradigm shift toward autonomous decision-making. As Noé Achache, Head of AI Engineering at Theodo, explained, traditional LLM implementations follow predictable paths—call an API, process the response, branch left or right based on predetermined logic. Agentic systems, however, operate with a fundamentally different philosophy: give them access to tools, data, and objectives, then let them determine the optimal path forward.
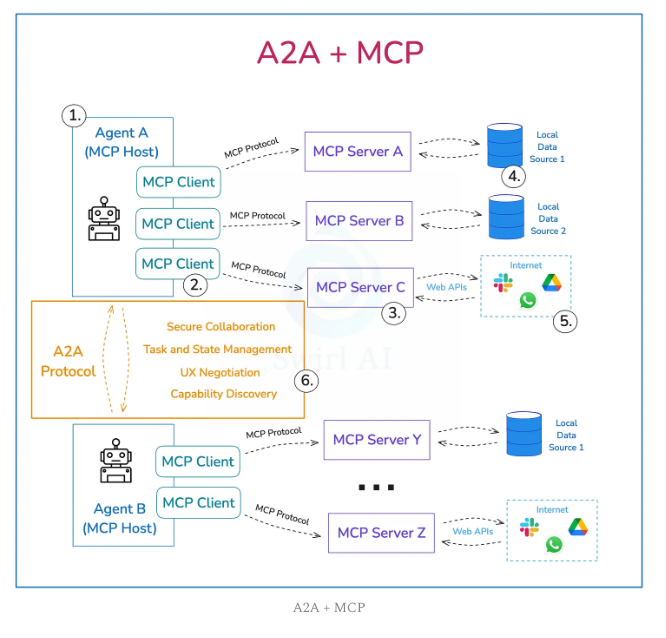
This distinction becomes crucial when considering protocols like MCP (Model Connection Protocol) and A2A (Agent-to-Agent), which have emerged as the connective tissue enabling this new ecosystem.
MCP, launched by Anthropic in late November 2024, has already spawned thousands of community-built servers in just six months—a testament to both its utility and the voracious appetite for AI automation across industries.
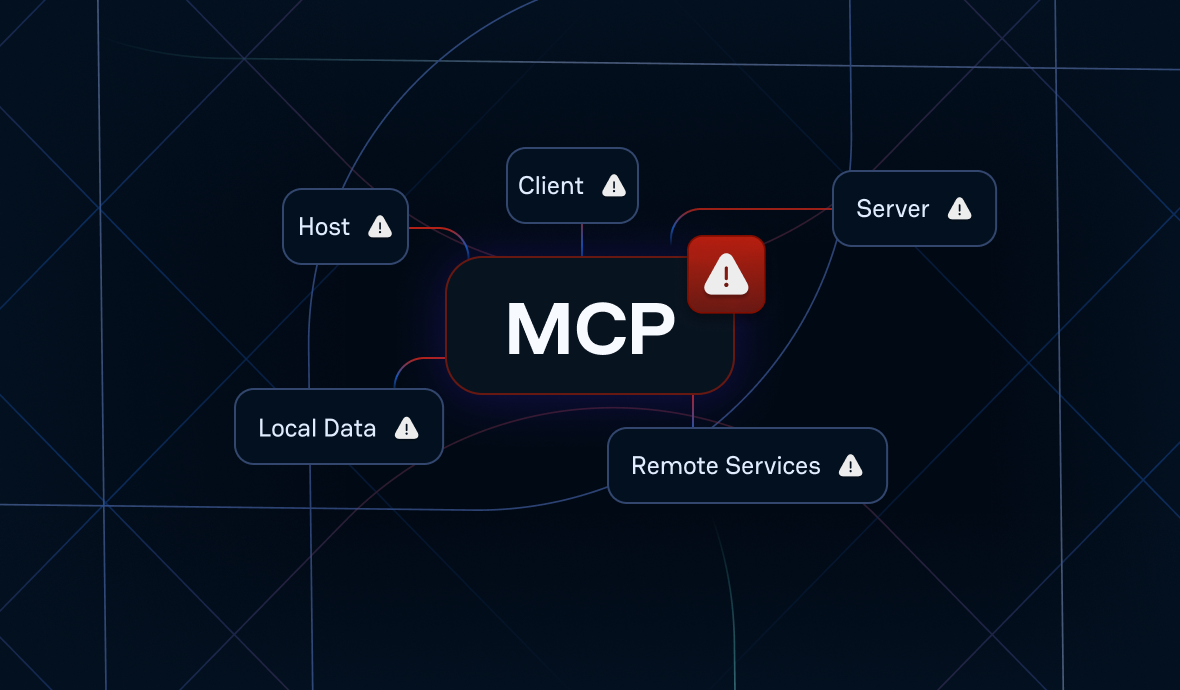
The democratization aspect cannot be overstated. Where previous automation technologies required specialized technical knowledge, agentic AI tools are accessible to anyone who can articulate their needs in natural language. This accessibility is driving adoption rates that dwarf previous technology cycles, creating what panelists described as both an unprecedented opportunity and a looming crisis.
The Traffic Surge: When Bots Become the New Normal
Gilles Walbrou from DataDome brought sobering statistics to the discussion. His company, which has been tracking bot traffic since 2015, has witnessed an explosion in AI-driven web traffic. What started as a manageable stream of automated requests has evolved into a torrent that's reshaping how websites think about security and access control.
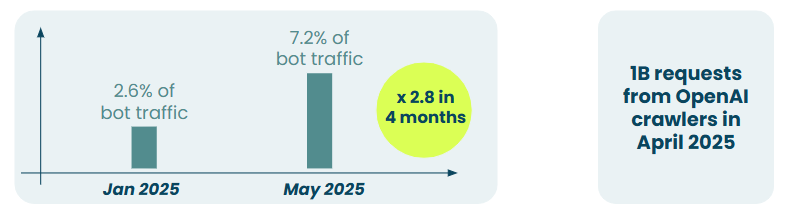
The challenge extends beyond simple volume. Traditional bot detection relied on behavioral patterns that remained relatively static over time. AI agents, however, can adapt, learn, and modify their approaches in real-time. This creates an arms race between detection systems and increasingly sophisticated automated actors, some benevolent, others decidedly not.
Notably, industry responses are starting to emerge: Cloudflare just launched a marketplace that allows websites to charge AI bots for scraping their content, an initiative that could shift both the economics and the security dynamics of bot-driven traffic (read more on TechCrunch). Yet as Walbrou emphasized, the fundamental challenge remains: distinguishing between legitimate automation and malicious activity in an environment where the lines are increasingly blurred.
The Identity Crisis: When Machines Outnumber Humans
Perhaps the most profound security implication discussed was the explosion of non-human identities (NHIs) within enterprise environments. Arnault Chazareix drew a compelling parallel to the microservices revolution that began fifteen years ago, noting how each new service required its own authentication mechanisms and access controls. Agentic AI is triggering a similar multiplication, but at an exponentially greater scale.
Every AI agent requires credentials to function. Every MCP server needs authentication tokens. Every automated workflow demands access to the systems it manipulates. The result is a sprawling landscape of machine identities that can quickly outnumber human users by orders of magnitude, creating what security professionals are calling "secret sprawl"—a distributed ecosystem of credentials that's increasingly difficult to inventory, monitor, and secure.

This proliferation isn't merely a scaling problem; it's a fundamental shift in the attack surface. Unlike human identities, which follow predictable patterns of creation, modification, and deactivation, machine identities often exist in a perpetual state of ambiguity. They're created for specific projects, forgotten when those projects evolve, and left dormant with their original permissions intact.
Secrets Management for Ephemeral AI Agent Identities
While traditional identity systems focus on user authentication, ai agent identity management presents unique challenges around credential lifecycle and secrets security. Unlike static service accounts, agentic AI systems require dynamic credential provisioning that can scale to thousands of ephemeral agents without creating security vulnerabilities.
The core challenge lies in managing API keys, certificates, and authentication tokens for agents that may exist for minutes or hours. Each AI agent requires secure access to multiple services, from cloud APIs to database connections, yet traditional secrets management approaches create bottlenecks and security gaps. When agents are created just-in-time, their credentials must be provisioned instantly, rotated automatically, and revoked immediately upon task completion.
Attack Vectors Targeting AI Agent Credentials
AI agents present unique attack surfaces that traditional security models fail to address adequately. Unlike human users who can recognize phishing attempts or suspicious access requests, autonomous agents operate based on programmed logic, making them vulnerable to sophisticated credential-based attacks.
The most critical vulnerability involves ai agent identity compromise through exposed secrets in code repositories, container images, or environment variables. Attackers specifically target AI agent credentials because these often have elevated privileges across multiple systems and lack the behavioral monitoring applied to human accounts. Once compromised, agent credentials can be used to access sensitive data, manipulate AI decision-making processes, or pivot to other systems within the enterprise.
Supply chain attacks represent another significant threat vector. Malicious actors can inject compromised credentials into AI agent dependencies, libraries, or training data pipelines. These attacks are particularly dangerous because they can remain dormant until specific conditions trigger malicious behavior, making detection extremely difficult through traditional monitoring approaches.
The Democratization Dilemma: When Everyone's a Developer
One of the most fascinating aspects of the current AI revolution is how it's democratizing software creation through what the panel termed "vibe coding."
This phenomenon, where non-technical users can generate functional code through natural language prompts, represents both a tremendous productivity opportunity and a significant security risk.
As the discussion revealed, tools like GitHub Copilot can inadvertently generate insecure code, embedding vulnerabilities or exposing secrets in ways that might not be immediately apparent to users who lack deep security training. The panel highlighted emerging threats like "slop squatting," where malicious actors create packages with names commonly hallucinated by AI systems, waiting for unsuspecting users to download and execute compromised code.

The challenge is compounded by the speed at which AI-generated solutions can move from proof-of-concept to production. Traditional security review processes, designed for human-paced development cycles, struggle to keep up with the velocity of AI-assisted creation. This creates a dangerous gap where insecure code can proliferate faster than security teams can identify and remediate it.
Building Guardrails for the Agentic Future
Despite these challenges, the panel remained optimistic about solutions emerging to address agentic AI's security implications. A key trend they identified is the centralization of AI access through internal proxies and gateways—what some organizations are implementing as "LiteLLM" architectures that route all AI interactions through monitored, controlled channels.
Organizations looking to implement robust AI security frameworks can now reference the newly released OWASP AI Testing Guide, which provides a comprehensive methodology for systematically assessing AI systems across various dimensions including adversarial robustness, privacy, fairness, and governance (learn more about the guide).
These centralized approaches enable several critical security capabilities: mandatory guardrails for all AI interactions, comprehensive audit trails, automated detection of personally identifiable information (PII), and the ability to enforce organizational policies consistently across all AI use cases. The upcoming EU AI Act, which takes effect in August, will further incentivize such approaches by requiring high-risk AI providers to analyze, understand, and test their systems comprehensively.
The panel also discussed the emergence of specialized security agents—AI systems designed specifically to review and improve the security posture of other AI-generated content. This meta-approach to AI security represents a fascinating evolution where the technology itself becomes part of the solution to its own risks.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture for Agentic AI Systems
Zero Trust principles become even more critical when applied to agentic AI systems, where traditional perimeter-based security models completely break down. AI agents operate across distributed environments, making autonomous decisions that can impact multiple systems simultaneously, requiring a fundamentally different approach to ai agent identity management.
The implementation begins with treating every AI agent as an untrusted entity that must continuously prove its identity and authorization. This means implementing certificate-based authentication for agent-to-service communication, with short-lived certificates that rotate automatically. Each agent interaction must be verified against current policies, with real-time risk assessment based on the agent's behavior patterns and requested resources.
Dynamic policy enforcement becomes essential, where access decisions are made based on contextual factors including the agent's current task, data sensitivity levels, and environmental conditions. For example, an AI agent processing financial data should have different access patterns than one handling marketing analytics, even if both agents originate from the same deployment pipeline.
The Path Forward: Security in the Age of Agents
As the SecDays France roundtable concluded, participants shared their most exciting agentic AI use cases while acknowledging the responsibility that comes with this power. From automating complex business processes to unlocking previously inaccessible unstructured data, the potential applications seem limitless.
Yet the overarching message was clear: agentic AI is not just another technology to be secured—it's a fundamental shift that requires rethinking how we approach identity, access, and risk management. The security community's response must be equally transformative, embracing new methodologies while maintaining the fundamental principles that have guided cybersecurity for decades.
As one panelist aptly summarized: "We are all builders, and we are all becoming security-aware."
In the age of agentic AI, this dual identity isn't just beneficial—it's essential for navigating the extraordinary opportunities and unprecedented risks that lie ahead.
The conversation at SecDays France highlighted that while agentic AI represents uncharted territory, the fundamentals of security remain constant: inventory your assets, monitor continuously, and build governance into every layer of your technology stack. Only by embracing these principles can organizations safely harness the revolutionary potential of autonomous AI systems.
FAQ
How does agentic AI change the landscape of identity and secrets management?
Agentic AI introduces a proliferation of non-human identities (NHIs), requiring dynamic, scalable secrets management. Unlike static service accounts, AI agents are often ephemeral, demanding just-in-time credential provisioning, automated rotation, and immediate revocation. This shift increases the complexity of inventorying, monitoring, and securing secrets across distributed environments.
What are the main attack vectors targeting AI agent credentials?
Attackers exploit exposed secrets in code repositories, container images, and environment variables to compromise AI agent identity. Supply chain attacks, such as injecting malicious dependencies or compromised credentials, are increasingly common. These attacks can grant unauthorized access to sensitive systems or manipulate AI-driven processes, often evading traditional monitoring.
How can organizations implement Zero Trust for agentic AI systems?
Zero Trust for agentic AI requires treating every AI agent as untrusted, enforcing continuous identity verification and dynamic policy enforcement. Certificate-based authentication, short-lived credentials, and real-time risk assessment are essential. Monitoring agent behavior and automating credential revocation further reduce the risk of lateral movement or privilege escalation.
What role does GitGuardian play in securing agentic AI identity and secrets?
GitGuardian provides automated secrets discovery, lifecycle management, and real-time monitoring for AI agent credentials. By integrating with deployment pipelines, it detects new agents, provisions secure credentials, and monitors for exposed secrets. This ensures robust AI agent identity management and reduces the risk of credential leakage or misuse.
How can organizations address the risk of "secret sprawl" with agentic AI?
To combat secret sprawl, organizations must inventory all non-human identities, automate secrets rotation, and enforce strict governance over credential usage. Continuous scanning for exposed secrets, centralized audit trails, and policy-driven access controls are critical. Solutions like GitGuardian help maintain visibility and control as agentic AI scales.
Why is AI agent identity verification critical in distributed, multi-cloud environments?
In distributed, multi-cloud environments, AI agent identity verification ensures that only authorized agents access sensitive resources. With agents operating autonomously across diverse platforms, robust verification—such as certificate-based authentication and automated secrets management—prevents unauthorized access and enforces compliance across complex infrastructures.