OpenClaw (formerly known as Clawdbot and Moltbot) is an open-source, self-hosted AI agent that operates directly on your local machine. It acts as your 24/7 personal assistant, and easily integrates with popular messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Slack, enabling it to execute tasks and take actions, going beyond simple conversational interactions.
It is a personal assistant that you can interact with using messages to automate a whole range of tasks. Agent skills are published at https://clawdhub.com/ and allow to easily extend OpenClaw. Using dozens of integrations, you can:
- sort emails and reply to them
- review pull requests
- summarize daily meetings
- book sport activities
- plan weekly meals for the family, and order groceries online
- Write code and deploy applications on your behalf
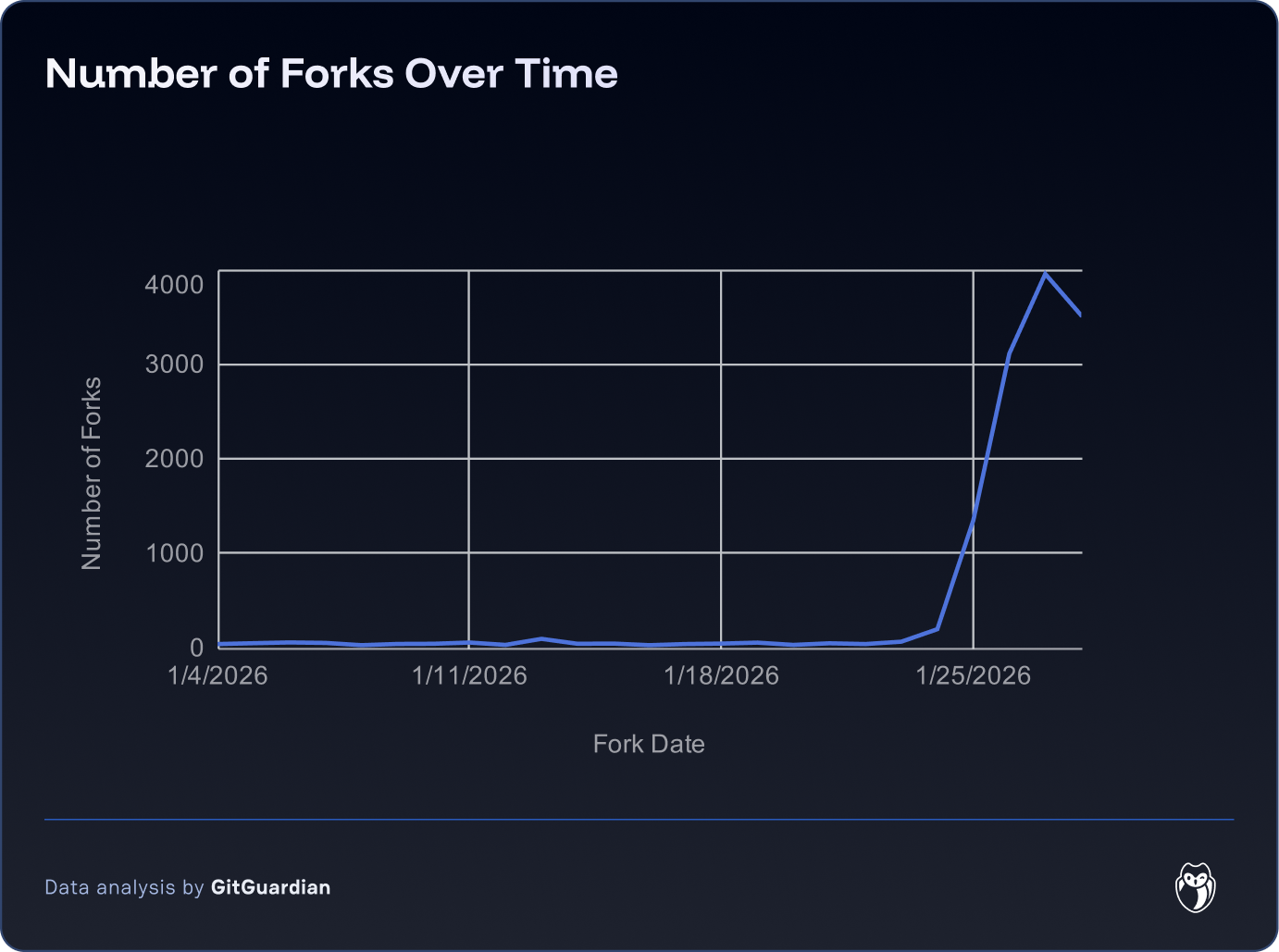
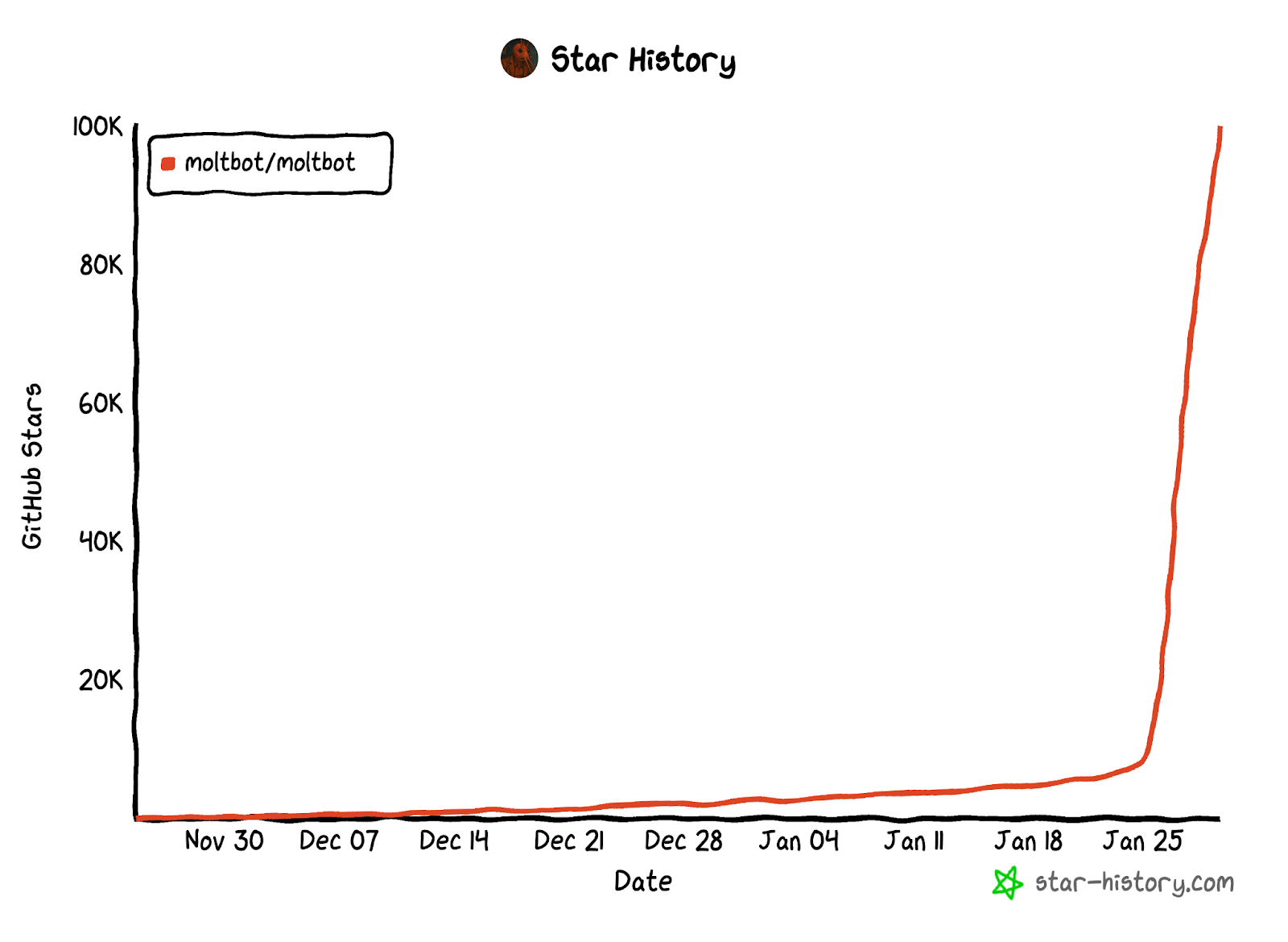
OpenClaw versatile and automated actions make it an extremely powerful tool whose adoption has continued to grow since its release in November 2025. Its usage went viral on January 24 2026, when the number of daily forks on GitHub went from 50+ to 3000+. The project's star count mirrored this explosive growth: OpenClaw gained a record-breaking 17,830 stars in a single day, ultimately crossing 85,000 stars within weeks—the fastest growth trajectory in GitHub history.
Workspaces & Leaked Secrets
A OpenClaw / Moltbot workspace is the agent's home (defaults to ~/clawd) - designed as a git repository for backup and sync. It provides the agent with persistent memory and a dedicated space for executing tools and tasks.
The documentation recommends treating the workspace as private storage and strongly encourages users to save it in private GitHub repositories. One section of the documentation is even dedicated to the risks associated with hardcoded secrets.
However, as might be expected, some people make mistakes and push their workspaces to public repositories - including secrets.
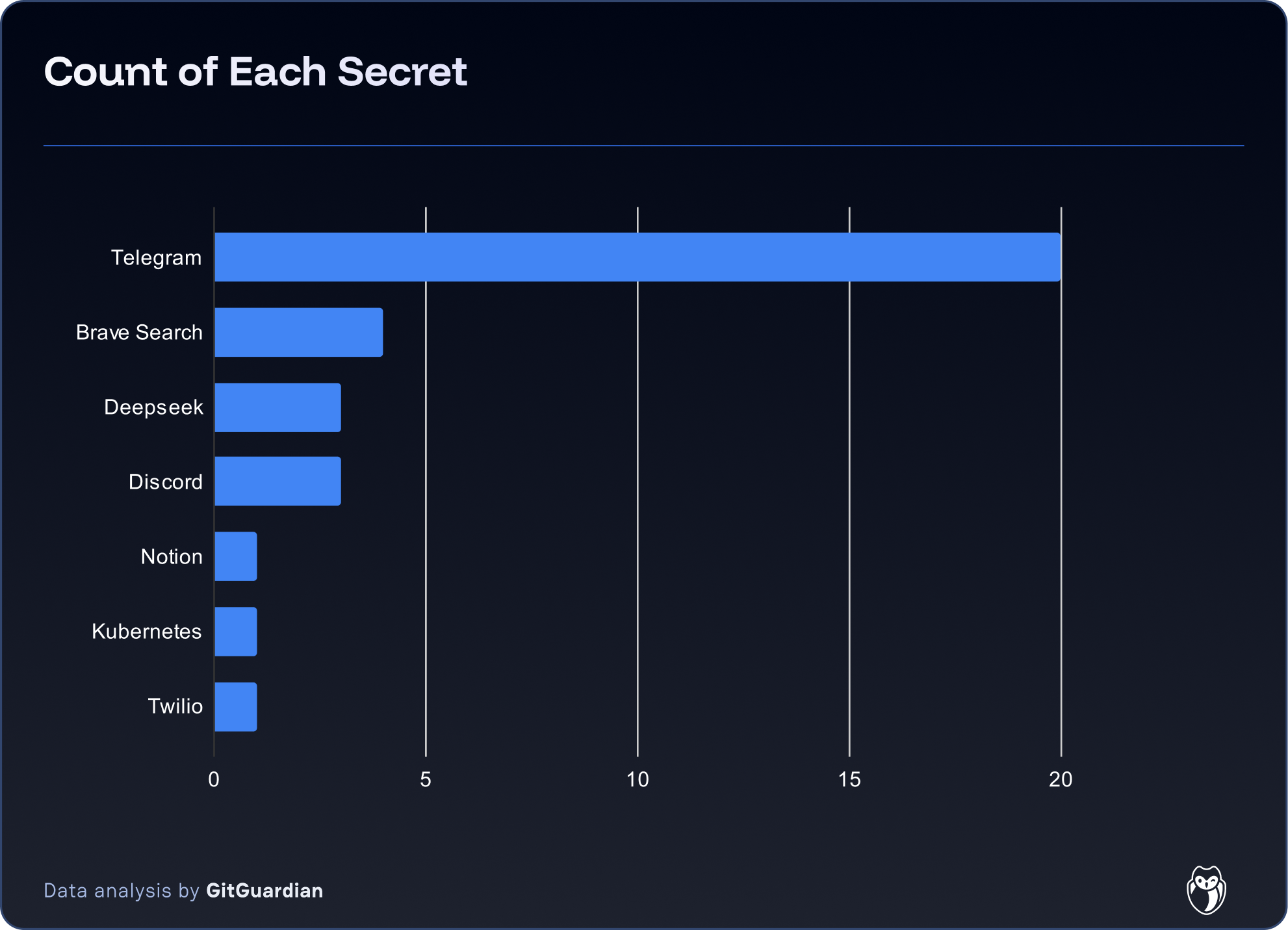
Since November, GitGuardian has detected 181 unique secrets, leaked from repositories with names containing either the clawdbot or moltbot keywords. At the time of writing, 65 secrets were still valid – 30% are Telegram Bot tokens, the easiest solution to interact with OpenClaw / Moltbot.
Among these secrets, two caught our attention: a Notion Integration token and a Kubernetes User Certificate. Leaked on January 24, the first one gave access to the entire corporate documentation of a healthcare company. The second, leaked on January 18 gave full privileged access to a Kubernetes cluster of a fintech company, used to host a OpenClaw/ Moltbot instance. Inside the repository, other credentials were leaked, including for a private Docker images registry. Following these discoveries, we performed responsible disclosures to their owners.
From the standpoint of proactive detection, our Good Samaritan program immediately identified and notified by email 38 developers responsible for the leaks. Unfortunately, as of writing, most secrets are still valid.
DockerHub also contains public images containing secrets related to OpenClaw / Moltbot. The first leak was detected on January 15, followed by several images every day. Now, 18 are still valid. Here, the types of secrets vary. We find GitHub tokens, AWS IAM keys, and Cloudflare tokens. This provides interesting information about the likely uses of OpenClaw / Moltbot for automating cloud infrastructure-related tasks.
Protecting OpenClaw Users: The ggshield Skill
While the OpenClaw documentation includes a dedicated security section warning users about the risks of hardcoded secrets, the proposed mitigation relies primarily on .gitignore rules—a pattern-based approach that fails silently when users forget to add sensitive files or when credentials end up in unexpected locations.The reality is that OpenClaw installations contain multiple sensitive files by design:
The nature of an AI agent's work makes preventing credential leaks challenging: the agent creates files, captures tool outputs, and logs session transcripts that may inadvertently include credentials pasted by users or fetched from external sources.
Running ggshield against a typical OpenClaw configuration directory immediately reveals the problem:
> ~/.clawdbot/clawdbot.json: 1 secret detected
>> Secret detected: Generic High Entropy Secret
Validity: No Checker
27 | "auth": {
28 | "mode": "token",
29 | "token": "d6e2bd8e********************************922c7e89"
|____________________apikey____________________|
From Passive Documentation to Active Prevention
To address this gap, we developed a ggshield skill for OpenClaw. Once installed, users can ask their assistant to scan the workspace for leaked credentials:
- "Check if my workspace contains any hardcoded secrets"
- "Scan my staged changes before I commit"
- "Set up a pre-commit hook to catch secrets automatically"
Important limitation: The skill runs on demand—it requires the user to prompt it. It does not automatically scan on commit or push. For users who want automated protection, the skill can install a git pre-commit hook that blocks commits containing detected secrets. The following are illustrative real-world use cases:
- Auditing the workspace:
"Scan my workspace for any secrets" Detects credentials in session logs, generated scripts, or files the agent created during tasks—before they ever reach git history.
- Pre-commit validation:
"Check my staged changes for secrets" Fast scanning of what's about to be committed, catching credentials before they enter version control.
- Setting up guardrails:
"Install a pre-commit hook to catch secrets" One-time setup that automatically blocks future commits containing detected credentials—the only automated protection the skill provides.
Installing the ggshield Skill
Prerequisites:
- ggshield CLI installed (see installation docs)
- A GitGuardian API key (see how to get one)
- The GITGUARDIAN_API_KEY environment variable set in your shell
Install via npx:
npx molthub@latest install ggshield-scannerThe skill is installed into your OpenClaw / Moltbot workspace's skills/ directory. Start a new session for the agent to pick it up:
# Verify the skill is loaded
clawdbot skills list
# You should see:
# ✓ ready │ 📦 ggshield-scanner │ Detect 500+ types of hardcoded secrets…Closing the Loop
The leaked secrets we detected from OpenClaw/Moltbot workspaces could have been prevented if users had access to integrated secret scanning. With the ggshield skill, OpenClaw users can ask their AI assistant the same question they'd ask a security-conscious colleague: "Is this safe to push?"—and get an answer backed by GitGuardian's detection engine before the damage is done. The skill is available on ClawdHub at ggshield-scanner, and the source code is published at https://github.com/GitGuardian/ggshield-skill.


![Shai-Hulud 2.0 Exposes Over 33,000 Unique Secrets [Updated Nov, 27]](/content/images/size/w600/2025/11/shai-hulud--2--1.png)




