One leaked API key can bypass millions in security investments. And it’s surprising how easily those keys end up exposed.
Jump directly to the list of the tools 🛠️ 👇
Modern development moves fast:
- CI/CD pipelines push hundreds of commits daily
- Developers work across multiple repos
- Infrastructure-as-code means secrets live in more places than ever
GitGuardian's 2025 State of Secrets Sprawl report found 23.8 million secrets were leaked on public GitHub repositories in 2024 alone. That's a 25% jump from the year before.
That’s not the worst part, though. 70% of secrets leaked in 2022 are still active today. These are live credentials sitting in git history, just waiting to be found.
Many secret scanning tools catch these leaks before they become breaches. SAST (Static Application Security Testing) tools only look for security vulnerabilities, but secrets detection software hunts for compromised credentials: AWS access keys, database passwords, SSH private keys, OAuth tokens, and anything else that could grant unauthorized access to your systems.
How Secret Scanning Works
Most real-time scanning tools use three techniques:
- Pattern matching looks for known secret formats. An AWS access key, for example, always starts with "AKIA" followed by 16 characters. These signatures make automated detection possible across billions of commits.
- Entropy detection catches high-randomness strings that look like generated secrets even when they don't match known patterns. This helps find custom API keys and internal tokens that wouldn't show up in pattern libraries.
- Context-aware validation reduces false positives by checking what's around a potential secret. Is it in a test file? Is there a comment saying "example key"? Smart scanners use these signals to separate real leaks from noise.
The hard part is balancing detection accuracy with alert fatigue. A tool that catches everything but buries your team in false positives isn't much better than one that misses half the real secrets.
What Makes a Good Secret Scanning Tool in 2026
Not all secrets scanners are built the same. Here's what matters when you're evaluating options:
- Continuous scanning vs. scheduled scanning makes a huge difference in mean time to detection. Triggered scanning that runs on every commit catches leaks in seconds. Automated scans that check entire repositories might take hours or days to flag the same issue.
- Detector breadth determines what you actually catch. Generic password detection matters as much as cloud provider keys. You need coverage for AWS, GCP, Azure, internal tokens, database credentials, and everything developers might hardcode.
- Integration depth goes beyond just connecting to GitHub. Can you scan GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure DevOps? What about Jira tickets, Slack channels, container images, and CI/CD artifacts? Secrets sprawl across the entire software development lifecycle, and your scanning needs to keep up.
- Prioritization and triage separate enterprise tools from basic scanners. Risk scoring, policy rules, and severity classification help teams focus on what matters instead of drowning in test keys and false alarms.
- Remediation workflows are where most tools fall short. Detection is useless if you can’t do something about it. The best platforms include playbooks for secret rotation, integration with ticketing systems, and guided steps that help developers fix issues fast.
- Machine learning for false positive reduction is non-negotiable. Even great pattern-matching produces noise. AI secrets detection tools that learn from your environment cut alert volume while maintaining accuracy.
- Reporting and compliance features matter for regulated industries. Audit trails, dashboards showing exposure trends, and evidence that sensitive data are continuously monitored help meet SOC 2, ISO 27001, and similar frameworks.
Still, scalability tends to be the bigger issue for enterprise security teams. Some tools works great for 10 developers but collapse under the weight of 500+ engineers across dozens of code repositories and multiple cloud environments.
Best Secret Scanning and Detection Tools for 2026
Now, let’s start looking at the tools. Each section covers what the platform does, who it's built for, and where it shines (or falls short).
GitGuardian
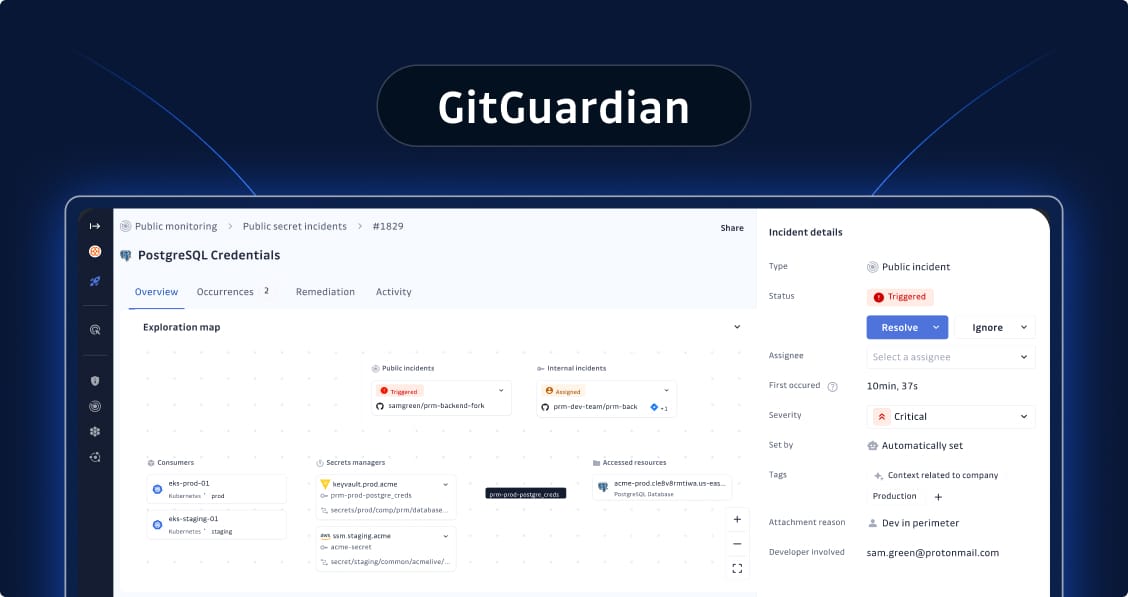
GitGuardian is an enterprise-grade secrets security platform that scans across the entire SDLC: source code, CI/CD pipelines, containers, IaC files, and even public GitHub history, as well as collaboration tools such as Jira or Slack. It's built for organizations that need comprehensive detection combined with governance and remediation features to fix what gets found.
Core features:
Real-time and historical git scanning across all major VCS platforms
550+ specific detectors plus ML-powered generic secrets detection
Multi-source scanning beyond code: Jira, Slack, container registries, and more
Incident prioritization with risk scoring and policy-based triage
Automated remediation playbooks and vault integration
Public GitHub monitoring that searches 6-8+ years of history for leaked sensitive information
Native integrations: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, major CI/CD tools, and secrets managers
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Best-in-class detection accuracy - 550+ detectors with industry-leading coverage | Premium features like public monitoring require paid tiers |
| Enterprise governance features - Audit trails, RBAC, developer feedback loops | Free version limited to very small teams |
| Strong remediation focus - Not just detection, actual incident resolution | |
| Public monitoring - Catches secrets leaked in personal repos (6-8+ years of history) | |
| Multi-source scanning - Beyond git: Docker, Slack, Jira, Confluence, logs | |
| ML-powered false positive reduction - 50% FP reduction through machine learning | |
| 317+ validity checks - Automatically verifies if secrets are active | |
| Saves 23+ hours per team weekly - Through automated remediation workflows | |
| Incident lifecycle management - Timeline tracking, regression detection, collaboration | |
| Breach detection - Honeytoken support for breach monitoring | |
| NHI governance - Secret inventory and risk assessment for non-human identities |
Pricing
Free tier available. Team and Business plans for growing organizations. Enterprise pricing customized for large deployments.
Enterprise fit
Excellent for organizations with 500+ developers, multi-cloud environments, or regulated industries where audit trails and compliance matter. The only secrets security platform purpose-built for complete detection, remediation, and governance at enterprise scale.
Website
Gitleaks (Open Source Tool)
Gitleaks is a popular open source tool for scanning git repositories. While it provides basic scanning capabilities, it lacks the enterprise governance and remediation features needed for production secrets security programs at scale.
Core features:
Git history scanning with configurable regex rules
140 secret types with regex and entropy filters
CI/CD integration
Custom rulesets for internal secret formats
Baseline scanning to track new vs. existing issues
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Completely free and open source | No validity checks - Can't verify if secrets are active |
| Easy to get running quickly | High false positives - Entropy detection creates noise |
| Strong community-contributed rule sets | No incident management UI - Detection only, no workflows |
| Good for baseline scanning without vendor lock-in | No remediation automation - Zero help with fixing issues |
| No real-time alerting - Misses developer notifications | |
| Limited scanning scope - Can't scan Docker, Slack, Jira, logs | |
| Single server limitation - No distributed scanning | |
| No enterprise governance - Missing SSO, RBAC, audit trails | |
| Software maintenance slowing - Development pace has decreased |
Pricing
Free and open source. Some vendors wrap Gitleaks in commercial offerings with added features.
Enterprise fit
Works as a starting point for evaluating risk or as a supplementary scanner. Organizations serious about secrets security need platforms like GitGuardian that provide complete incident lifecycle management, remediation automation (saving 23+ hours per team weekly), and enterprise governance at scale.
Website
https://github.com/gitleaks/gitleaks
Truffle Security Enterprise
Truffle Security is known for git repository scanning with entropy-based detection. While it offers basic scanning capabilities, it lacks the enterprise remediation features and accuracy needed for production secrets security programs.
Core features:
Scheduled scanning of entire repositories (not delta-based)
800+ detectors that create significant alert fatigue
Git history scanning with entropy detection
Basic CI/CD integration
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Open source core with community support | Scans entire repos vs deltas - Longer mean time to detection (MTTD) and higher resource consumption |
| Entropy detection catches some custom secrets | 800+ detectors overwhelm teams - Creates significant alert fatigue and noise |
| Forager provides limited public monitoring (1 year coverage) | No ML-powered false positive reduction - vs GitGuardian's 50% FP reduction through machine learning |
| No generic secrets detection - Missing passwords and usernames detection | |
| No breach detection capabilities - No Honeytoken support | |
| Limited public monitoring - Only 1 year coverage, no identity stitching (vs GitGuardian's 6-8+ years) | |
| No developer-centric remediation playbooks - Missing guided workflows | |
| Basic scanning tool - Detection only, not a complete remediation platform |
Pricing
Open source core with paid enterprise features and support.
Enterprise fit
Works as a basic scanning tool for historical audits. TruffleHog detects but leaves you to figure out remediation and buries you in false positives along the way. Organizations serious about secrets security need platforms like GitGuardian that provide ML-powered accuracy, complete incident lifecycle management, and automated remediation workflows.
Website
https://trufflesecurity.com/trufflehog
GitHub Advanced Security
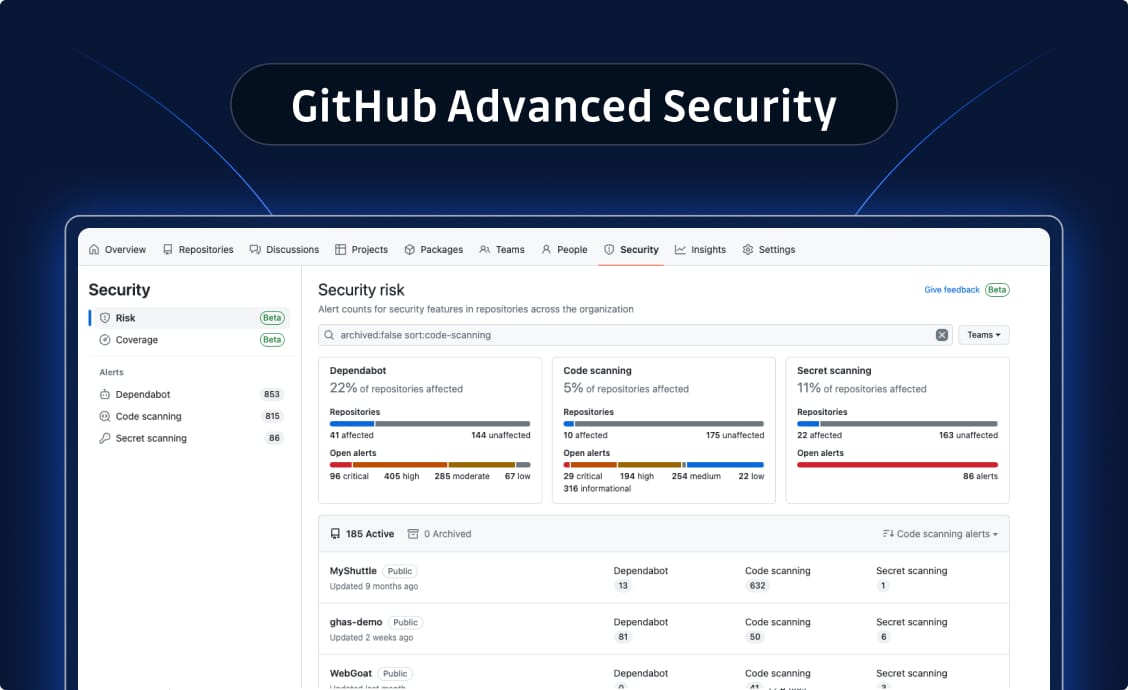
GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) is GitHub's native security offering that provides code scanning, secret scanning, and dependency review capabilities. As part of the GitHub ecosystem, it offers integrated security features for organizations standardized on GitHub Enterprise.
Core features:
- Secret scanning for GitHub repositories with 160+ detectors
- Push protection to prevent secrets from being committed
- Historical scanning of Git repository history
- Native integration with GitHub's security dashboard
- Custom pattern support via regular expressions
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Native GitHub Enterprise integration | GitHub-only - No GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps support |
| Built-in push protection | Weak generic detection - 7 detectors (beta), high false positives |
| SAML SSO and enterprise auth | No governance - Missing incident assignment and playbooks |
| SIEM integration (Splunk, Sentinel) | No pre-commit/pre-push hooks - Server-side only |
| Unified security dashboard | No CI/CD integration - Can't scan Jenkins, CircleCI, etc. |
| Audit logs for compliance | Limited validity checks - Only 4 token types vs 317+ |
| Available for on-premises | No severity scoring - Manual prioritization required |
| No sensitive file detection - Misses .env, .pem files | |
| Repositories only - Can't scan Docker, logs, Slack, Jira | |
| No incident management - Missing timeline and workflows | |
| Repository-level grouping - Duplicate alerts across repos |
Pricing
Priced per active committer on a monthly or annual basis. Requires GitHub Enterprise Cloud or GitHub Enterprise Server. Contact GitHub sales for enterprise pricing.
Enterprise fit
Works well for organizations fully committed to the GitHub ecosystem who want basic secrets detection as part of their existing GitHub investment. However, enterprises with multi-platform development environments, complex remediation workflows, or requirements for comprehensive secrets governance across their entire attack surface will find significant gaps in coverage and capabilities. Most security-mature organizations supplement GHAS with specialized secrets security platforms to address these limitations.
Website
https://docs.github.com/en/code-security/secret-scanning
Core features:
Git history scanning with configurable regex rules
CI/CD integration
Custom rulesets for internal secret formats
Baseline scanning to track new vs. existing issues
Aikido Security
Aikido is a unified application security platform that combines secrets detection with SAST, SCA, and other AppSec capabilities in one tool.
Core features:
Integrated scanning: secrets alongside code and dependency analysis
CI/CD pipeline integration
Centralized dashboards
Policy management across security domains
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| All-in-one approach reduces tool sprawl | Secrets detection depth - May not match specialized tools |
| Fast setup and decent coverage | Trade-off between breadth and depth |
| Good for teams wanting consolidation over specialization |
Pricing
Tiered SaaS plans based on team size and feature needs.
Enterprise fit
Strong option for mid-market teams that prioritize unified tooling and want good-enough secrets coverage alongside other AppSec scans.
Website
Yelp - Detect Secrets
Detect Secrets (originally built at Yelp) is a lightweight scanner focused on preventing commits with secrets before they hit your repository. While useful for basic pre-commit enforcement, it lacks enterprise capabilities.
Core features:
Plugin system supporting only 20 types of secrets out-of-the-box
Performs entropy checks to detect generic secrets
Baseline comparison to track new findings
Pre-commit hooks for local enforcement
Validity checks for fewer than 5 detectors
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Simple and developer-friendly | Only 20 secret types - vs 550+ in GitGuardian |
| Great for pre-commit enforcement | No VCS integrations - No GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps |
| Baseline approach focuses on new issues | No incident management interface - Zero UI or workflow capabilities |
| No incident lifecycle management | |
| No remediation playbooks - Detection tool only | |
| No real-time alerting - Missing email notifications | |
| No collaboration features - No developer workflows | |
| No enterprise features - No SSO, RBAC, audit logs, or API | |
| Limited scanning - Can't scan Docker, Slack, Jira, logs | |
| Detection only - No help with fixing issues |
Pricing
Free and open source.
Enterprise fit
Useful for team-level enforcement and developer education. Not sufficient alone for enterprise-wide secrets governance. Best used as a prevention layer in combination with platforms like GitGuardian for comprehensive detection and remediation.
Website
https://github.com/Yelp/detect-secrets
Spectral (Checkpoint)
Spectral, acquired by Check Point, combines AI-assisted detection with developer-focused workflows. While it offers IaC security features, it requires significant custom development for VCS integrations and lacks native enterprise capabilities.
Core features:
Claims 2,500+ built-in detectors (no detailed list provided)
ML-based generic secrets detection
Git and CI/CD scanning via CLI
IaC misconfigurations detection for AWS, Azure, GCP
Policy controls via spectral.yaml configuration file
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Strong IaC security focus alongside secrets detection | Custom integration required - Must build own GitHub app and AWS Lambda functions |
| CI/CD integration support | No validity checks - vs 550+ types in GitGuardian |
| Natural fit with Check Point products | No presence checks - Can't verify secret removal from git history |
| No Docker scanning - Missing container image support | |
| No native Slack/Jira scanning - Must build custom connectors | |
| No Bitbucket or Azure DevOps - Limited VCS support | |
| No post-receive hooks - Missing continuous monitoring | |
| No native PR check runs | |
| Incomplete unified view - Relies on user declarations | |
| No restricted developer view - Missing scoped access |
Pricing
SaaS model with enterprise bundle options.
Enterprise fit
Suitable for organizations with IaC security needs who can invest engineering resources in building custom integrations. Organizations needing native VCS integrations, comprehensive incident management, and automated remediation typically choose platforms like GitGuardian that provide these capabilities out-of-the-box.
Website
HashiCorp Vault Radar
Vault Radar is HashiCorp's dedicated secrets scanning and discovery product, separate from HashiCorp Vault itself (which GitGuardian integrates with for remediation). Radar finds unmanaged or leaked secrets across developer tools and repositories.

Core features:
Git repository scanning across GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure DevOps
Detection of hardcoded secrets and unmanaged credentials
Risk prioritization and alert workflows
Optional hybrid/on-premises scanning via Vault Radar Agent plus CLI and IDE tools
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Strong fit for HashiCorp-standardized organizations | Better as extension of HashiCorp ecosystem |
| Supports hybrid deployment models | Public monitoring and SDLC-wide scanning - May lag best-of-breed specialists |
| Natural integration with Vault for remediation |
Pricing
Commercial SaaS as part of HashiCorp Cloud Platform (HCP). Enterprise and tiered pricing models.
Enterprise fit
Best for large, complex organizations with multi-cloud and multi-repository environments that already rely on HashiCorp Vault and want integrated secrets discovery plus lifecycle governance.
Website
https://www.hashicorp.com/products/vault/hcp-vault-radar
GitLab Secret Detection
GitLab Secret Detection uses an analyzer containing the Gitleaks tool to scan repositories. While convenient for GitLab users, it's limited to GitLab-only environments and lacks the depth needed for enterprise secrets security.
Core features:
Pipeline scanning integrated into merge requests
90 types of secrets based on Gitleaks rulesets
Pre-defined rule sets for common secrets
Policy enforcement within GitLab workflows
Historical scans configured to run as pipeline jobs
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Seamless UX for GitLab users | GitLab-only - No GitHub, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps coverage |
| Simple enablement with GitLab Ultimate | Only 90 secret types - vs 550+ in GitGuardian |
| No additional vendor complexity | False-positive prone entropy detection - No pre/post-filters |
| Very limited generic detection - Only API keys with "API-" prefix | |
| Cannot deactivate detectors - No CLI or UI control | |
| No sensitive file detection - vs 22 file names + 14 extensions in GitGuardian | |
| GitLab pipelines only - vs 8 providers in GitGuardian | |
| No PR check runs - Missing merge request scanning | |
| No incident management - Missing severity scoring, assignment, status tracking | |
| No automated remediation - Missing playbooks and developer feedback loops |
Pricing
Included with GitLab Ultimate subscription.
Enterprise fit
Strong choice if GitLab is your central VCS and you don't need scanning outside that ecosystem. Works best when paired with additional tools for non-GitLab environments.
Website
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/application_security/secret_detection/
Cycode
Cycode positions itself as a complete SDLC and ASPM (Application Security Posture Management) platform. While it offers broad security coverage, its secrets detection capabilities are secondary to its platform approach and lack key features that enterprises need for comprehensive secrets security.
Core features:
Multi-source scanning across VCS, CI/CD, and cloud environments
ASPM Marketplace with ConnectorX integration capability
Secrets detection as one module within broader AppSec suite
Policy enforcement across development lifecycle
Support for AWS CodeCommit, Bitbucket Cloud, GCP Cloud Source
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Unified platform for consolidated tooling | Far fewer detectors - vs GitGuardian's 550+ detectors |
| ASPM-ready with native integrations | No validity checking - Cannot verify if secrets are active |
| Decent multi-source coverage (Slack, Jira, S3) | No breach detection - Missing Honeytoken support |
| Full VCS integration support | No public GitHub monitoring - GitGuardian scans 6-8+ years |
| No generic secrets detection - Missing passwords and usernames | |
| No NHI governance - Missing secret inventory and risk assessment | |
| No secrets manager integration - Cannot automate remediation | |
| No customizable remediation guidelines - Missing UI customization | |
| Full developer onboarding required - vs GitGuardian's external incident links | |
| Cannot verify secret removal - Missing git history verification | |
| No developer feedback collection - Orchestration workflows incomplete |
Pricing
Commercial SaaS with enterprise tiering.
Enterprise fit
Suitable for organizations prioritizing unified SDLC platforms over best-of-breed secrets security. However, enterprises serious about secrets governance typically choose specialized platforms like GitGuardian.
Website
Pricing: Commercial SaaS with enterprise tiering.
Enterprise fit: Suitable for organizations prioritizing unified SDLC platforms over best-of-breed secrets security. However, enterprises serious about secrets governance typically choose specialized platforms like GitGuardian.
Website: https://cycode.com
Legit Security
Core features:
Pipeline visibility and posture management
Secrets detection across build and deployment stages
Policy enforcement for software supply chain security
Integration with existing DevOps tools
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive SDLC-wide view | Secrets detection depth varies - vs specialized tools |
| Strong fit for governance at scale | Pipeline security focus - Not secrets-first approach |
Pricing
Enterprise SaaS pricing.
Enterprise fit
Excellent for AppSec teams that need to govern CI/CD pipelines at scale and want secrets detection integrated into that broader mission.
Website
Aqua Security Trivy
Trivy is a widely-used open source scanner that covers containers, infrastructure as code, and secrets detection. It's become a standard tool in cloud-native environments.
Core features:
Container image scanning
IaC scanning for Terraform and Kubernetes manifests
Secrets detection within containers and code
Extensive CI/CD plugin support
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Excellent for containerized and Kubernetes workloads | Secrets detection not as deep - vs dedicated secrets scanners |
| Broad coverage across multiple security domains | Better as part of layered approach - Not standalone secrets solution |
| Strong community support |
Pricing
Free and open source core. Aqua offers enterprise versions with additional features and support.
Enterprise fit
Great for cloud-native and Kubernetes-heavy teams. Should be paired with dedicated secrets scanning for comprehensive coverage across the SDLC.
Website
Prisma Cloud (Palo Alto Networks)
Prisma Cloud is Palo Alto Networks' comprehensive CNAPP platform. It includes secrets detection as part of its code-to-cloud security posture management.
Core features:
Secrets detection integrated into broader cloud workload protection
IaC scanning with secrets checks
Compliance alignment across cloud environments
Unified risk visibility
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Enterprise-grade CNAPP with secrets detection bundled | Secrets detection is one capability among many |
| Strong compliance and audit capabilities | Less specialized - For git history analysis and developer workflow remediation |
Pricing
Commercial SaaS with enterprise CNAPP pricing models.
Enterprise fit
Very large organizations buying comprehensive CNAPP/CSPM solutions who want decent secrets detection bundled with broader cloud security.
Website
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/prisma/cloud
SentinelOne
SentinelOne is primarily an endpoint detection and XDR platform with growing capabilities around identity protection and credential security.
Core features:
Threat detection across endpoints
Identity misuse alerts
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Strong SOC and security operations integration | Not a purpose-built secret scanner |
| Good for credential protection via XDR stack | Lacks coverage and depth - vs dedicated secrets detection tools |
Pricing
Enterprise security bundles, typically sold as part of broader XDR/EDR packages.
Enterprise fit
Works for organizations where secrets risk is one component of a broader security operations strategy that's managed through a unified platform.
Website
Cider Security (Prisma Cloud)
Cider Security is an ASPM platform that aggregates security signals from multiple scanners into unified risk views that include secrets detection.
Core features:
Signal aggregation from multiple security tools
Centralized prioritization across SAST/SCA/secrets/IaC findings
Policy-based risk scoring
Integration as Prisma Cloud's application security layer
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Centralized view reduces alert fatigue | Secrets detection not the primary focus |
| Includes secrets alongside CI/CD, SAST, SCA, IaC signals | Only valuable as orchestration layer - Requires existing scanners |
Pricing
Commercial SaaS with enterprise ASPM/Prisma tiering.
Enterprise fit
Large enterprises standardizing on Prisma Cloud who want secrets detection inside an end-to-end ASPM orchestration approach.
Website
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/prisma/cloud/cloud-code-security
How to Choose the Right Secret Scanning Tool for Your Organization
The right tool depends on your organization's size, technical stack, and security maturity. Here's a practical framework:
For Startups and Small Teams
Focus on ease of use and getting CI guardrails in place quickly. Open source secret scanning tools like Gitleaks or Detect Secrets give you baseline protection without budget pressure. Pair them with native tools from your VCS provider.
The goal is to prevent accidental exposure without creating friction that slows shipping. Developer education matters a lot more than elaborate governance workflows.
For Mid-Market Organizations
Integration depth and manageable false positives become critical. You need coverage beyond just git repositories (like Jira, Slack, container images). Tools like GitGuardian, Spectral, or Aikido provide breadth without overwhelming small security teams.
Look for automated remediation guidance and reasonable alert volumes. At this stage, you're balancing protection with team capacity. A tool that finds everything but requires manual triage of 1,000 alerts per week just isn't sustainable.
For Enterprise
Governance, policy enforcement, multi-cloud support, and multi-repository scale become non-negotiable. You need centralized visibility, role-based access, audit trails, and the ability to handle hundreds of repositories across different VCS platforms.
Enterprise secret scanning tools need to support prevention (pre-commit and CI/CD scanning) and detection (historical and public real-time monitoring).
These organizations typically need platforms like GitGuardian, HashiCorp Vault Radar, or comprehensive ASPM solutions that include secrets as part of broader application security governance.

Evaluation Checklist
When comparing tools, prioritize these factors:
- Detection quality: Test accuracy on your actual codebases. What's the true positive rate? How well does it catch generic secrets like hardcoded passwords?
- False positive ratio: Alert fatigue kills security programs. How much noise does the tool generate? Does it learn from your environment?
- Integration breadth: Can you scan code on all your VCS platforms? What about CI/CD, containers, IaC, and collaboration tools?
- Remediation depth: Does it just alert, or does it guide developers through rotation? Can it create tickets automatically? Does it integrate with your secrets manager?
- Reporting and compliance: Can you prove continuous monitoring for auditors? Are there dashboards showing exposure trends over time?
- Public repository monitoring: Does it catch secrets leaked in personal repos by your employees? This is often a huge blind spot.
- Non-human identity coverage: Does the tool help you inventory and manage service accounts, API keys, and machine identities?
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Yes, having the right tool matters, but implementation determines whether it actually protects you. Here's how to roll out secret scanning for coverage you can trust:
Layered Rollout Strategy
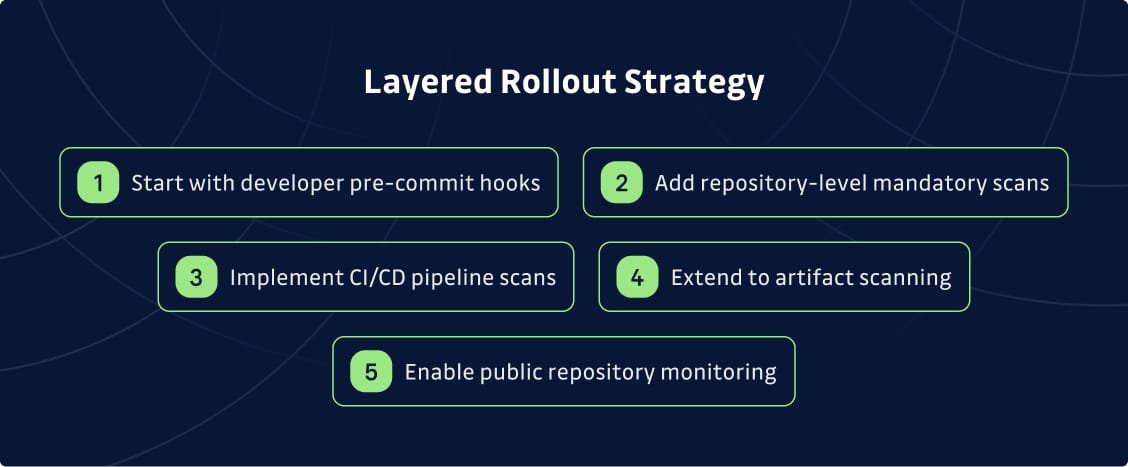
Here’s a step-by-step approach to rolling this out:
- Start with developer pre-commit hooks using tools like Git-Secrets or Detect Secrets. This catches secrets before they hit your repository and creates immediate feedback for developers.
- Add repository-level mandatory scans that run on every push. This is your safety net when local hooks get bypassed.
- Implement CI/CD pipeline scans that check for dynamic secrets in build artifacts, configuration files, and deployment packages. Secrets don't always live in source code—they hide in Docker images and IaC templates too.
- Extend to artifact scanning for containers and infrastructure code. Tools like Trivy or Bridgecrew handle this well.
- Enable public repository monitoring to catch secrets leaked in personal repos. Developers often copy code from work to personal projects without realizing they've included credentials.
Process Best Practices
Get this right, and you’ll turn potential disaster into controlled containment:
- Define your policy clearly. What counts as a secret? Are test credentials excluded? Do expired API keys trigger alerts? Make these decisions upfront to avoid confusion later.
- Set ownership. Who triages alerts: AppSec, IAM, DevOps? Who's responsible for rotation? Unclear ownership leads to ignored findings.
- Automate critical workflows. High-severity leaks should create tickets automatically and notify the right teams. Speed matters when credentials are exposed.
- Train developers on secure alternatives. Scanning finds problems, but education prevents them. Teach developers how to safeguard sensitive data with secrets managers, environment variables, and proper key management.
- Track metrics that matter. Mean time to remediation, recurrence rates, and exposure trends over time. These metrics show whether your program is actually reducing significant security risks.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes happen, but knowing the most common ones is the first step in preventing them:
- Alert fatigue from false positives kills adoption. If developers ignore your alerts because 80% are noise, the tool isn't helping. Prioritize accuracy and tune aggressively.
- Bypassable controls create false confidence. Pre-commit hooks are great, but can be disabled. Don't rely on them alone—layer multiple automated security checks.
- No rotation playbook means detected secrets stay valid. Finding a leaked key is only valuable if you can rotate it quickly. Document the process and automate where possible.
The Future of Secret Scanning
Times are changing, and these are the trends reshaping secrets detection heading into 2026:
- AI-assisted detection and validation is moving beyond basic pattern matching. Machine learning models can understand context, reduce phantom detections, and even suggest remediation approaches based on similar past incidents. We're seeing this already in tools like GitGuardian and Spectral, but expect it to become standard across the category.
- Expansion into containers and infrastructure as code reflects where secrets actually live. Developers increasingly define infrastructure through code, and every Terraform template or Kubernetes manifest can contain hardcoded credentials. Secret scanning is expanding to meet the reality of modern development.
- Non-human identity governance is becoming core to secrets security. Organizations are realizing that service accounts, API keys, and machine identities far outnumber human credentials. Managing and monitoring these NHI secrets is non-negotiable, and you need a dedicated non-human identity secret scanning and governance tool.
- Continuous monitoring beyond VCS because git repositories are just one leak vector. Secrets show up in Jira tickets, Slack messages, wikis, shared documents, and monitoring tools. Comprehensive protection means scanning everywhere credentials might land (not just where code lives).
The goal isn't perfect detection—that’s impossible. It's more about reducing the window of exposure to the point where attackers can't reliably exploit leaked credentials. That means faster detection, automated remediation, and reliable governance that guarantees secrets don't stay valid long enough to cause damage.
More Security, Less Exposed Secrets
Credential leaks remain one of the most straightforward paths to a serious data breach. Secret scanning tools exist to catch those leaks before they're exploited, but not every tool will be the right fit for your use case.
Specialists like GitGuardian and TruffleHog offer deep detection and enterprise governance, while platform-native tools like GitHub Advanced Security and GitLab Secret Detection work well if you're tightly coupled to those ecosystems. Then, there are cloud-provider options like AWS Secrets Manager and Azure Key Vault that handle specific environments but need complementary scanning for broader SDLC coverage.
The right approach usually involves layering:
- A best-of-breed scanner for comprehensive detection and governance
- Integrated with your VCS platform's native capabilities
- Connected to your secrets manager for remediation
GitGuardian is built for this problem: catching leaked credentials across your entire development environment and helping teams fix them before attackers can exploit them.
Start for free today or schedule a demo with our team.