What Happened?
In early December 2024, the U.S. Department of the Treasury was breached through a compromised API key used by BeyondTrust to provide technical support to the department end-users. The threat actor was able to remotely access user workstations, as well as unclassified documents. This breach underscores the critical risks associated with compromised API keys and highlights the importance of securing third-party integrations to protect sensitive systems and data.
Events Timeline
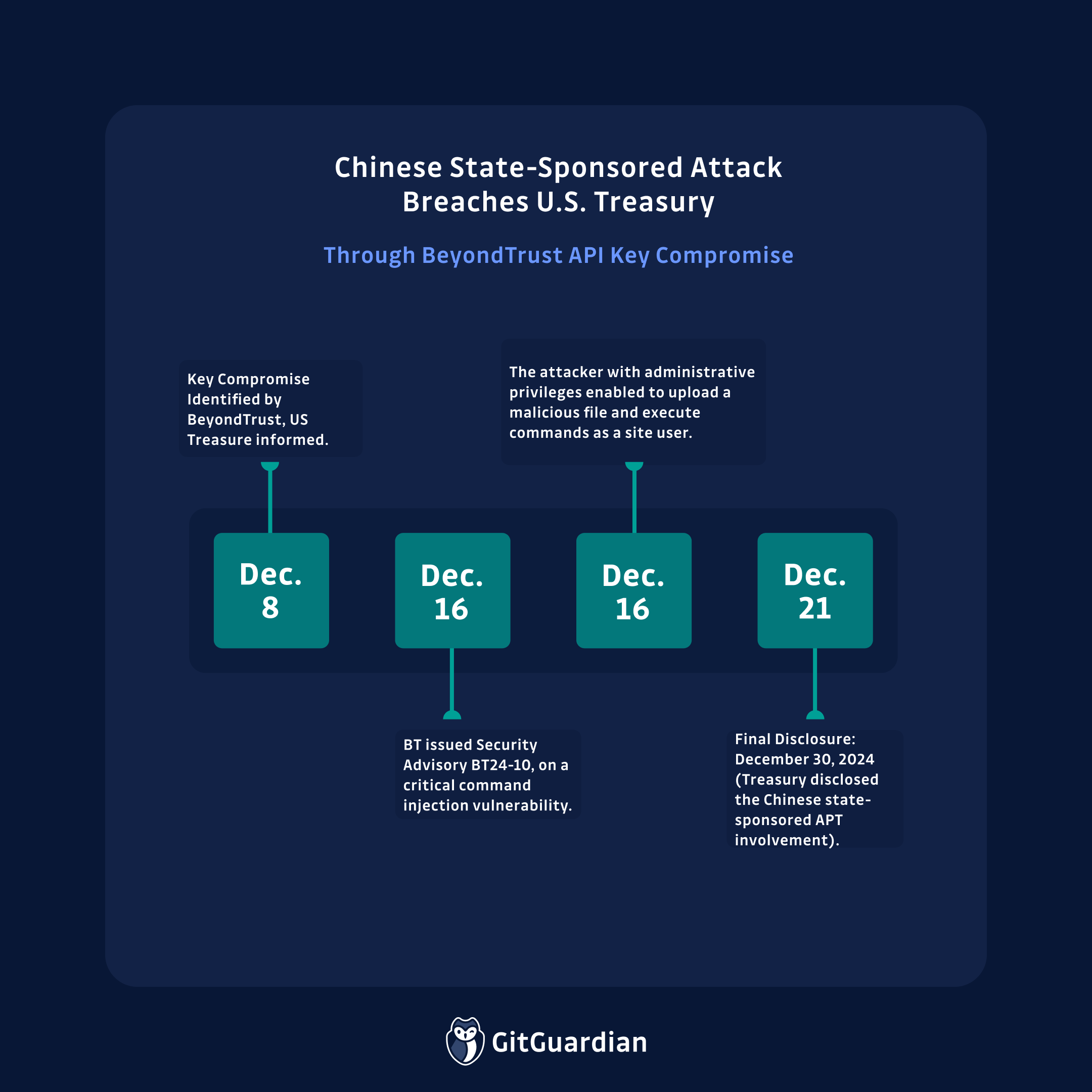
- December 2, 2024: BeyondTrust detected anomalous behavior and started investigating potential unauthorized access.
- December 5, 2024: BeyondTrust identified that an API key for their Remote Support SaaS had been compromised. The company revoked the compromised key, notified impacted customers, and suspended the affected instances.
- December 8, 2024: BeyondTrust informed the U.S. Department of the Treasury that attackers had obtained an API key used for a cloud-based service providing remote technical support.
- December 16, 2024: BeyondTrust issued Security Advisory BT24-10, addressing a critical command injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-12356) affecting all versions of their Privileged Remote Access (PRA) and Remote Support (RS) products up to version 24.3.1.
- December 18, 2024: BeyondTrust issued Security Advisory BT24-11, addressing a medium-severity command injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-12686) in PRA and RS. This issue could enable an attacker with administrative privileges to upload a malicious file and execute commands as a site user.
- December 30, 2024: The U.S. Department of the Treasury disclosed to lawmakers that it had been breached by a Chinese state-sponsored Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) actor. The attackers exploited the compromised BeyondTrust API key to access Treasury workstations and unclassified documents. The Treasury Department collaborated with the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the FBI to assess the impact of the breach.
Lesson Learned
As 2024 is upon us, this incident serves as a severe reminder of the devastating impact of compromised credentials. As demonstrated, attackers were able to bypass security measures using a valid leaked API key and access sensitive workstations and data. The breach highlights the urgent need for both service providers and end users to implement robust secrets management practices, especially secrets monitoring, to secure their supply chain.
More Breached Explained








![Shai-Hulud 2.0 Exposes Over 33,000 Unique Secrets [Updated Nov, 27]](/content/images/size/w600/2025/11/shai-hulud--2--1.png)




