Proprietary algorithms, sensitive client data, and advanced trading infrastructure are critical to hedge funds’ operations today. This growing reliance on technology also makes hedge funds prime targets for cyberattacks. For firms whose reputation, operations, and legal standing rely on strong security measures, securing critical assets is no longer optional - it’s an essential part of their strategy.
One of the most vulnerable access points is the mismanagement of secrets - credentials, API keys, tokens, and other sensitive information. Hardcoded secrets embedded directly in source code, pose a significant risk. If exposed, these secrets can cause severe financial and reputational damage. As cyberattacks due to secrets become more frequent, understanding and mitigating these risks is critical.
This article explains why hedge funds, perhaps more than many other industries, must prioritize secrets security, covering both safely stored and compromised secrets, to protect their assets and operations.
Hardcoded Secrets: A Growing Threat To Hedge Funds
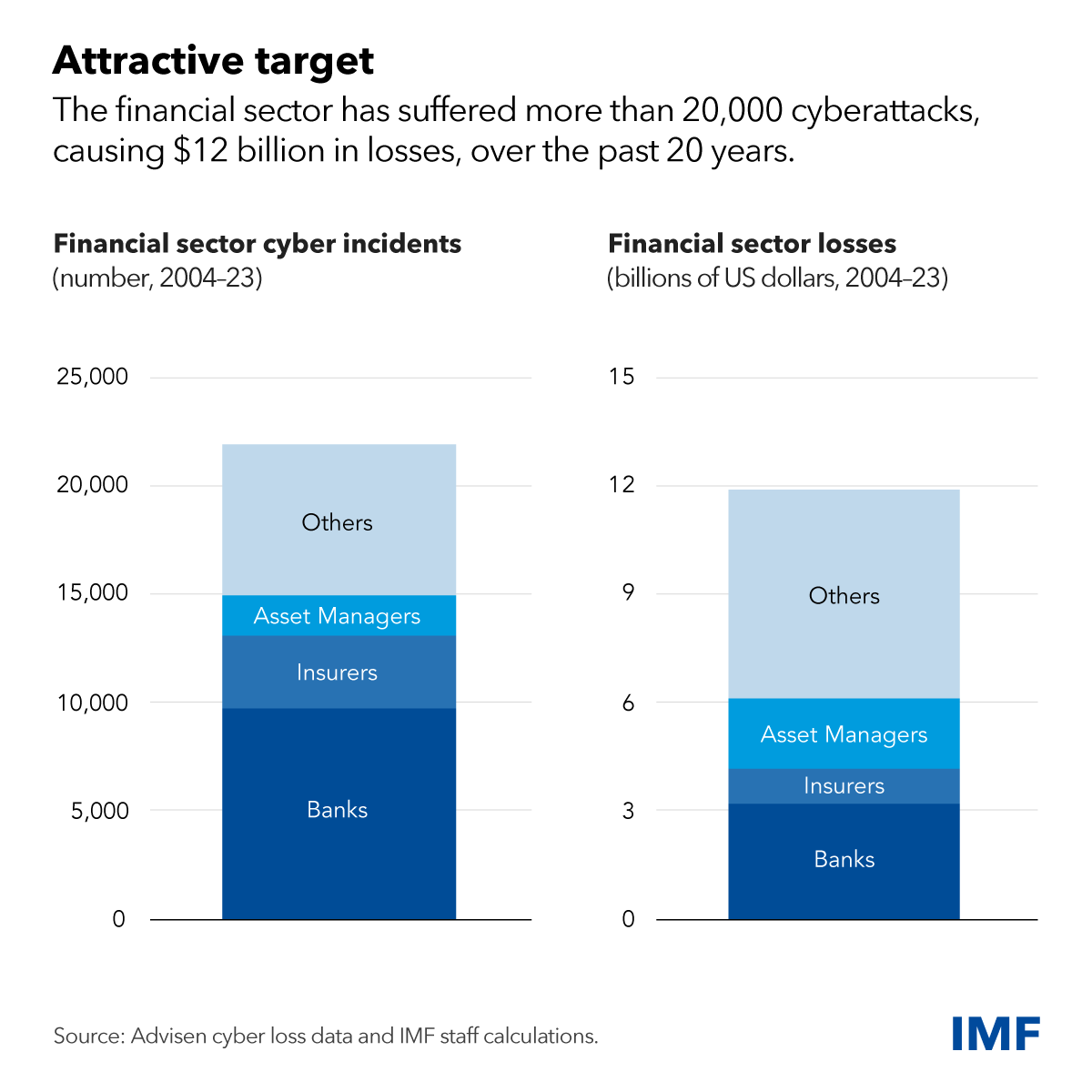
The leakage of hardcoded secrets has become a major concern in the financial industry and hedge funds are no exception. According to GitGuardian’s State of Secrets Sprawl report, more than 12 million secrets were exposed on GitHub in 2023 alone, a staggering four-fold increase over the last four years. For hedge funds, this is more than a technical vulnerability. It directly threatens their operational security, client confidentiality, and competitive position. Secrets accumulate more quickly with more developers, increasing the processing time, remediation cost, and exposure risk.
High-profile breaches like those of Uber and Toyota demonstrate the devastating effects of hardcoded secrets being leaked. For hedge funds, even a single exposed credential can lead to unauthorized access to critical trading systems, compromising sensitive data or interfering with trading operations. The stakes are particularly high. Statistics show that over 60% of breaches result from “people issues,” such as weak or compromised credentials, which highlights the need for comprehensive secrets security efforts. Secrets security requires active involvement across the entire organization to create a culture of awareness and vigilance.
In addition to protecting trading systems, hedge funds must secure specialized internal platforms, such as investor databases, deal-pipeline management tools, and advanced data analytics applications. These platforms store sensitive client information and proprietary trade data that, if exposed, could lead to financial losses and damage investor trust.
On July 3, 2022, the CEO of crypto-currency giant Binance warned of a massive breach:
The bug? A fragment of source code containing the secret for a titanic database of personal information was allegedly copied and pasted onto a developer's blog of the Chinese CSDN network. Source
Whether secrets have been left in code because of malintent or negligence, they are always a boon for hackers. All sorts of playbooks can be deployed upon finding leaked credentials, even the most innocuous ones, such as a Twitter API key: from phishing to privilege escalation and data exfiltration.
Complex Secrets Lifecycle Management Across Environments
Like many other organizations, hedge funds rely on multiple secrets management solutions, including AWS Secrets Manager, Google Secrets Manager, HashiCorp, and others. This fragmented approach creates a significant risk of secrets sprawl and inconsistent management practices. The need to copy-paste credentials between different environments and vaults increases the chances of human error and unintentional exposure of sensitive information. This complexity makes it difficult for hedge funds to centralize or effectively monitor their secrets, leaving critical vulnerabilities open for exploitation. Without clear oversight and consistent practices, these risks just keep compounding.
The challenge is in establishing visibility and control over a firm’s secrets inventory. Without a reliable "source of truth," hedge funds struggle to answer basic questions:
- Where are secrets stored?
- Who has access to them?
- When were they last accessed?
This lack of visibility creates gaps that delay responses to incidents, leaving vulnerabilities exposed for too long. Tracking secrets across multiple repositories becomes a slow, inefficient process, increasing the potential for overlooked issues.
Why Hedge Funds Are Especially Vulnerable
Hedge funds today operate increasingly like tech companies. They employ large teams of developers to continuously build and refine proprietary algorithms that drive competitive trading strategies. But they often lack the same robust cybersecurity frameworks as larger financial institutions.
They face unique risks compared to other industries due to their tech-heavy approach and their reliance on speed, sensitive algorithms, and the significant regulatory pressures they face.
A. Protecting Proprietary Algorithms: The “Crown Jewels”
A hedge fund’s competitive advantage largely depends on its proprietary algorithms—intellectual property developed through rigorous research and significant investment. These algorithms power strategies like high-frequency trading (HFT), where millisecond decisions make or break profits. Secrets embedded in these algorithms—credentials for data feeds or trading APIs—can be exploited if exposed. For a hedge fund, this could mean financial theft, market manipulation, or a loss of competitive edge.
Speed is the ultimate edge
To keep this advantage, algorithms must execute trades at lightning speed, processing massive volumes of data and responding to market changes instantly. This is critical not just for HFT but for:
- Arbitrage: Taking advantage of brief price discrepancies across markets
- Real-time news analysis: Algorithms capable of reacting instantly to breaking news
- Foreign exchange: Reacting quickly to currency fluctuations
Timing is critical, particularly during market opening and closing hours when trading volume and volatility are at their peak. If systems fail during these key periods, it can lead to significant missed opportunities and financial loss. Protecting these algorithms from exposure or disruption is essential to preserve a hedge fund’s operations and value.
B. Safeguarding Investor Data and Confidential Information
Hedge funds handle vast amounts of sensitive client information and financial data for high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors which must be safeguarded at all costs. This data includes personal identifiers, detailed financial portfolios, and proprietary investment strategies. Any breach would cause severe reputational damage, and financial loss, and potentially lead to legal consequences—not only for the hedge fund but for its clients as well.
Given their high-profile clients, hedge funds are prime targets for cybercriminals looking to exploit or ransom valuable data. Maintaining strong security standards is not only a regulatory mandate but also a business necessity to protect client trust and maintain the fund’s standing in the market.
Hedge funds also work with third-party service providers—custodians, brokers, and other service providers—who access their sensitive data. A breach in a third-party system can indirectly expose the fund’s information, underscoring the importance of a robust security strategy that extends across the fund’s interconnected network of vendors and partners.
Any disruption from a cyberattack that hinders trading operations impacts a hedge fund's ability to meet its fiduciary duty. As Edward Sadtler (consultant at Citi, ex-Headex Head of Intellectual Property, Sourcing & Technology Group at Schulte Roth & Zabel LLP) said in The Hedge Fund Journal,
“It is not just about alerting investors to data breaches. If, due to a cyberattack, systems are completely shut down for a week or two, and fund managers cannot trade, they cannot fulfill their fiduciary duty to investors”.
C. Balancing Developer Productivity with Security
Hedge funds rely on top talent to refine trading algorithms, and tools like GitHub Copilot and other AI coding assistants have become popular with their developers. It’s important for retaining current developers and attracting new ones. But with these productivity gains come risks.
Risks of AI Coding Assistants
Copilot presents several security concerns, including the risk of leaking sensitive information like API keys or passwords through code suggestions. Since Copilot is trained on public repositories, it may suggest insecure or outdated code practices that contain vulnerabilities. For hedge funds, using such tools without safeguards can lead to unintentional exposure of sensitive code or credentials.
Developers lack knowledge about the best practices. Implementing safeguards that secure sensitive information without slowing down developers is essential for fast-paced trading environments. Solutions that prevent secret leaks before they reach public repositories or version control systems can help hedge funds balance security with productivity.
D. Tools Adapted to On-Prem Environments and Compliance
While many hedge funds operate in highly controlled, air-gapped environments to reduce security risks, this isolation often limits access to cloud-native security tools. Solutions that can work effectively in such hybrid setups are highly valued as they can integrate smoothly with on-premise systems without compromising security.
E. Meeting Regulatory Pressure and Compliance
Hedge funds face strict regulatory scrutiny and may be subject to more rigorous regulation soon. Regulatory bodies such as the SEC, FCA, FINRA, and IRS in the U.S. and U.K., along with global mandates like GDPR for funds handling EU resident data, impose a variety of compliance obligations. These requirements are increasingly being enforced with an eye toward investor protection, focusing on areas such as data privacy, transaction transparency, and robust cybersecurity protocols.
Moreover, compliance demands often become even more specific depending on the financial products the fund aims to launch. Regulatory agencies scrutinize each new offering to ensure it meets local requirements, meaning funds must obtain regulatory clearance for these products before they reach the market. As a result, hedge funds must be proactive in aligning their data and operational security with the evolving regulatory landscape.
How Hedge Funds Can Tackle the Secrets Challenge
Tackling the challenge of secrets sprawl requires a multi-faceted approach, here’s how hedge funds can address this challenge effectively.
A. Complete Visibility Across the Development Lifecycle
To keep secrets secure, hedge funds need deep integrations and coverage of their overall perimeter. With development teams often working across specialized areas like equities and exchanges, gaining insight into code changes and potential vulnerabilities is critical. Comprehensive monitoring across platforms like GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure Repos, as well as CI/CD tools and container images, helps hedge funds control where secrets live and how they’re used.
With the shift toward remote and hybrid work post-pandemic, secrets can leak through various channels outside traditional development environments. Hedge funds should consider monitoring communication tools like Slack and Jira, as secrets are sometimes unintentionally shared there. Real-time detection, immediate remediation, and detection of historical leaks prevent secrets exposure that could impact trading operations and the fund’s performance.
B. First-class Detection with the Best Recall/Precision Ratio
For secrets security, precise detection is essential. The ideal platform offers first-class detection capabilities that can identify a wide variety of secret types, from specific provider credentials to more generic patterns. The platform should employ a combination of regular expressions, entropy checks, and machine learning techniques to maximize recall and precision, ensuring that a broad range of secrets are detected, including custom patterns.
The platform should also conduct validity and presence checks to filter out false positives and confirm whether exposed secrets are still valid. By minimizing false positives as much as possible, hedge funds avoid “alert fatigue,” keeping developers focused on the most critical secrets incidents without overwhelming them. High-precision detection supports faster development cycles, keeping projects on track while maintaining a high level of security.
C. Prioritized Remediation Within Development Workflows
Detecting exposed secrets is just the beginning. Hedge funds need efficient ways to handle remediation without slowing down operations or spending much of their resources’ time.
Incidents need to be created and assigned to the appropriate developer and team, with ownership identified. The platform should collect developer input on the secret, identify its occurrences, check validity, and analyze the application/service impact.
Automated severity scoring is another valuable feature, prioritizing incidents based on the type and potential exposure risk of each secret. This system allows hedge funds to address the most critical issues first.
The platform should pinpoint files for developers to fix, and track the progress to ensure the remediation process is successful and doesn’t impact functionality.
D. Shifting as left as possible
Developer adoption is a critical factor.
An ideal solution integrates into the developer’s workflow, providing feedback directly in tools like Visual Studio Code or within pull requests, helping teams remediate issues in real time. It should offer custom remediation messages, which guide developers on storing secrets in a secure vault or suggest other corrective actions. This encourages secure coding habits from the start, without developers having to leave the IDE.
E. Enterprise-Grade Capabilities: Reporting, Scalability, and Support
For hedge funds, a robust secrets security platform must be enterprise-ready, providing detailed reporting and risk analytics to track security progress and remediation efforts over time.
As funds grow, scalability is key. The platform should be able to accommodate expanding development teams, multiple repositories, various programming languages, and integrations with source control, CI/CD systems, and other productivity tools.
Deployment flexibility is another critical factor. Hedge funds often need on-premises solutions to meet compliance standards, but cloud-based options may be suitable for others. Seamless data export capabilities, through formats like CSV or API, allow hedge funds to integrate secrets management into broader security frameworks.
Dedicated support also plays a vital role, ensuring smooth POC, onboarding, offering custom scripts to implement the solution, lunch & learns, and helping teams address any complex challenges during rollout.
F. Integrating Secrets Managers
Phishing and social engineering attacks are common threats that target hedge funds. A practical defense against these attacks involves securely storing credentials in vaults or secrets managers.
Secrets security platforms that integrate with secrets managers or Vaults provide hedge funds with a consolidated approach to having visibility on the status of their secrets, and access control, helping to detect and manage “rogue” secrets that aren’t securely stored. These integrations support streamlined workflows for rotation and revocation, strengthening the hedge fund’s overall secrets management strategy without taking any resources bandwidth.
A Competitive Edge Through Secrets Security
Securing secrets is beyond just meeting compliance. It’s a competitive advantage. Hedge funds rely on their proprietary methods and client data for competitive positioning, and breaches can result in losses far greater than the cost of investing in a strong secrets security strategy.
GitGuardian offers comprehensive secrets protection—no one has tackled this problem like we have. With us, hedge funds can lock down their most valuable assets and build a security-first culture that reduces secrets risks and drives long-term resilience and growth.
Protecting secrets isn’t merely about stopping leaks—it’s about building a solid foundation for sustained success in this increasingly competitive market.